Models
Navigation: Main Page ➔ Models
Latest SysCAD Version: 25 October 2024 - SysCAD 9.3 Build 139.36522
Introduction
A SysCAD project consists of a number of independent process units, known as models, connected by pipes or links. Each model is documented independently and can be accessed from the following tables, or alternately, directly from SysCAD.
To access the Models Help from within SysCAD (with live internet access), simply click on the Model Help button in the Access window:
General Models
These models are used in most projects. They generally form the backbone of the project. All models are available with a standard license.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Steady State and Dynamic General Models | |
| Feeder-Cross Page Connector | A source or sink of material, or it can be used to connect streams on different flowsheets. |
| Tie | The tie can be used to join two or more streams, or to split a stream into a number of streams. It may have up to 20 inputs and 20 outputs. It may also contain reactions, makeups, vapour-liquid equilibrium (VLE) and/or general splitter (GM) sub-models. |
|
Steady State Only General Models | |
| Pipe | Pipe or material transfer model used to connect units. |
| Tank | A multi-purpose unit. Can contain reactions, heat exchanger, makeups or general splitter (GM) sub-models. |
|
Dynamic Only General Models | |
| Pipe - Dynamic | Pipe or material transfer model used to connect units in Dynamic Transfer mode. This may include flow restrictions. |
| Tank - Dynamic | A storage unit for material in Dynamic Transfer mode. Can contain reactions, heat exchanger, makeups, etc. sub-models. |
Energy Transfer Models
These models are used to transfer energy, or heat, from one stream to another. This may involve mass and energy transfer, or it may only involve energy transfer. All models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license except for the Flash Train functionality which is only available in Steady State. Most models require the Energy Balance add-on and some require an additional add-on as shown in the table below. Without Heat Calculations being enabled in the project, some of the functionality of these models will be restricted.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Barometric Condenser | Achieves vapour liquid equilibrium between an incoming liquor stream and a vapour stream at a user-defined pressure. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| Boiler | This is a simple steam boiler. Boiler Feed Water is first heat to the required Drum Pressure then superheated to the required outlet pressure and temperature. The unit will produce steam and blowdown streams and predict the energy required by the boiler, based on the drum pressure and superheated steam conditions. |
| Cooling Tower | This is a simple water evaporation model where water is evaporated to provide cooling. |
| Desuperheater | This is a simple steam desuperheater model where water is added to reduce the degree of superheat in steam. Can be used in steam line in a Flash Train. |
| Direct Contact Heater 2 | Improved Direct Contact Heater model with more options. Achieves vapour liquid equilibrium between incoming liquor and steam streams. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| Electrowinning Cell | The user defines the reaction by which the material is deposited onto the cathodes and the cell efficiency. The model calculates the energy requirements of the cell and the amount of heating, based on the enthalpy of reaction and the efficiency. |
| Evaporative Dryer | The Evaporative Dryer is used to remove the water from the solids in the feed stream. The model will use the user-defined moisture remaining in the cake to calculate the amount of water to be evaporated off. Any liquid impurities will remain in the cake moisture. The unit also allows for some solids loss with the evaporated moisture. |
| Evaporator (Crystalliser) | Achieves vapour liquid equilibrium for a defined set of conditions and allows the user to enable Reactions and/or Solubility to produce crystals or a precipitate. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| Falling Film Evaporator 4 | In a falling film evaporator, weak liquor is pumped to the top of the unit and distributed to the tubes where it runs down as a film. Steam is entered on the shell side, the condensation of the steam provides energy to heat and if hot enough, evaporate water from the weak liquor, thus concentrating the liquor stream. This is a replacement for the FFE2 model, with additional functionality of being able to connect the model to other flash train components or evaporators without having to implement pressure controllers. |
| Flash Tank 2 | As for Flash Tank, but also allows the user to add Reactions and Solubility to the unit and allows the user to enable or disable the Flash Train functionality in the unit. Also available for use in Dynamic solver. |
| Flash Train | This is not an independent unit. It is made up of other SysCAD units such as Flash Tanks and Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers. The Flash Train will attempt to obtain equilibrium across all of the individual units by varying the pressures and temperatures. This functionality is only available in Steady State. |
| Reactor (Gibbs FEM) | Modelling combustion and equilibrium using a Gibbs Free Energy Minimisation algorithm. |
| Hot Flash Tie | This model is used for mixing a very hot stream (hot air) with moist solids to create dryer solids, such as Calciner, Dryer. When the two streams mix, heat is transferred from the hot stream to heat up and flash the moisture in the solids stream, leaving no free moisture in the mixture if the temperature is hot enough. User can switch on the reactions sub model in the unit to perform other reactions in the unit, any sub models will take place after the initial feed mixing and flashing of moisture. |
| Multi-Stage Counter Flow Tie | This model is designed to emulate equipment that contacts a Gas stream with either a Liquid or Solid stream in counter-current flow. |
| Reboiler/Condenser Heat Exchanger | Available from Build 139.35250. The Reboiler/Condenser Heat Exchanger (RCX) is used to transfer heat from one stream to another. |
| Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger 2 | Used to transfer heat from one stream to another, with no direct contact between streams. Requires the user to know the Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient and the heat exchange Area. Allows user defined reactions in the tube side. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| Simple Condenser | This is a generic "heat exchanger" model without regards to its cooling media or equipment size. It can provide estimates of the Duty required to condense an amount of material, or alternatively, determine the amount of condensation for a given duty or temperature. |
| Simple Evaporator | This is a generic "heat exchanger" model without regards to its heating media or equipment size. It can provide estimates of the Duty required to evaporate an amount of material, or alternatively, determine the amount of evaporation for a given duty or temperature. |
| Simple Heater | This is a simplified model of the heat exchanger where only one side is simulated; the other side is reported as duty. |
| Simple Heat Exchanger | This is a simple model of a heat exchanger that is used to transfer heat from one stream to another, with no direct contact between streams. Requires the user to set the required temperature for the exiting stream from one side of the unit. The energy to achieve that change is transferred to the stream on the other side of the unit. |
| Steam Turbine | The steam turbine converts steam energy into shaft work, which can then be converted to electrical work through the generator. |
| Thermocompressor | This is a simple model of a Thermocompressor. It is a form of steam ejector in which a flow of high pressure (HP) primary steam is used to entrain low pressure (LP) secondary steam. The discharge stream is at an intermediate pressure between the high and low pressure steam flows. |
| Energy Transfer Models that require the Potash and Energy Balance Add-Ons | |
| Evaporator - Potash | Achieves vapour liquid equilibrium for a defined set of conditions and allows the user to enable Reactions and/or Solubility to produce salt crystals that can be washed in the Evaporator 'Leg'. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| OLD legacy models, these models may be discontinued in future builds, please consider changing to the suggested equivalent newer models | |
| Direct Contact Heater | This is a very simple Model. Achieves vapour liquid equilibrium between incoming liquor and steam streams. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. Please consider changing to Direct Contact Heater 2, which contains more options. |
| Falling Film Evaporator | This model has very limited functionality, please change to Falling Film Evaporator 4, which works as part of the flash train. |
| Falling Film Evaporator 2 | Please change to Falling Film Evaporator 4, which works as part of the flash train. |
| Flash Tank | Achieves vapour liquid equilibrium of the feed stream at a user-defined pressure. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. Please consider changing to Flash Tank 2, which contains more options. |
| Heat Exchanger | Used to transfer heat from one stream to another, with no direct contact between streams.
|
| Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger | General purpose heat exchanger. Used to transfer heat from one stream to another, with no direct contact between streams. Requires the user to know the Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient and the heat exchange Area. Can be used as a boiler/evaporator. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. Please consider changing to Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger 2, which contains more options. |
Mass Separation Models
These models are used to separate one or more feed streams into two or more discharge products. All models are available with a standard Steady State or Dynamic license. Some of these models are designed to handle incoming streams containing liquid and solids only, any vapour present will be lost. This will typically be reported in the unit as a vent.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Centrifuge - Batch Centrifuge | With the batch centrifuge the user may emulate washing the cake with 1 or 2 washes separately as in a batch process. The user defines the amount of moisture remaining in the centrifuge cake and the amount of solids in the filtrate. |
| Centrifuge - Disk Centrifuge | The user defines the amount of moisture remaining in the centrifuge cake and the amount of solids in the filtrate. |
| Filter - Belt Filter | Simulates a belt filter with any number of counter current wash stages. The user MUST enter data on the simple filtration wash losses, which is often difficult to obtain. Please consider using the Filter Press for most normal filter applications. |
| Filter - Drum Filter | Simulates a drum filter with wash water. The user defines the amount of liquid in the filter cake, as well as the fraction of wash water that bypasses through the cake. |
| Filter - Filter Press | Used to separate solids and liquids. The user may add a wash water stream. The user defines the amount of moisture in the filter cake, as well as the wash efficiency. |
| Flotation Cell | A simple model of a Flotation Cell that requires the user to define the primary species or element that is recovered to the concentrate. The model requires the user to define the primary species or element that is recovered to the concentrate stream. The user may then specify the recovery and grade or mass pull of the primary species/element. The recoveries of secondary species may also be defined by the user. Alternatively, the model can be used with PSD and the user can set the recovery to concentrate of each solid species with a size distribution in each size interval. The user may add an air stream. |
| General Separator | Used to split the feed stream(s) into a Vent stream and two user-defined streams. This is a very flexible model using the Solid-Liquid Separator sub-model. |
| Ion Exchange | The Ion Exchange model can be used to simulate reactions between a liquor stream and a solid phase of resin. |
| Reverse Osmosis (RO) | The Reverse Osmosis model can be used to simulate a reverse osmosis membrane process, often used in water treatment, especially for desalination of sea water. The user may specify the yield and efficiency of the process, as well as the outlet pressure requirements. |
| Solids Recovery Unit | The Solids Recovery Unit can be used to model a variety of solid recovery processes including flotation, magnetic separation and spirals. The model requires the user to define the primary species or element that is recovered to the concentrate and middlings streams (if connected). The user may then specify the recovery and grade or mass pull of the primary species/element. The recoveries of secondary species may also be defined by the user. Alternatively, the model can be used with PSD and the user can set the recovery to concentrate/middlings of each solid species with a size distribution in each size interval. |
| Solvent Extraction (Mixer Settler) | The Solvent Extraction model may use McCabe-Thiele equilibrium diagrams to determine the extent of transfer between phases, or the user may specify the extent of reaction. The model ensures that mainly aqueous phases leave via the aqueous stream and organic phases leave through the organic stream. |
| Thickener - CC Washer | This model is mainly used in the Alumina industry as the user must supply the Scandrett wash efficiency, which is used to calculate the user-defined species concentrations in the under and over flows. The model emulates a thickener with imperfect mixing. |
| Thickener - Classifier | The classifier mixes perfectly all the incoming feed streams and then, based on the user configuration, calculates the amount, temperature and composition of material reporting to the underflow and overflow. |
| Thickener - Thickener | The thickener model requires the user to define the solid split to the under and over flow in ProBal mode. The user may add Reactions and Makeups to the model, but it assumes 100% mixing efficiency. |
| Thickener - Underflow Washer | This model has the functionality to 'wash' the underflow stream of the thickener. The user may set the wash efficiency and enable Reactions and Solubility in the main section of the model and the Over and Under flow sections. |
| Thickener - Washer | This is the same as the thickener model, except that it also allows the user to set the mixing efficiency between the washer feed and side streams. |
| Thickener - Washers (CCD) | This single model simulates an entire CCD circuit. It can be used to quickly determine the concentration in the final over and under flow streams from a series of thickeners. The model is designed to be used as a quick means of determining the effect of differing numbers of stages or wash water ratio in a CCD circuit. |
| Dynamic Model with Surge | |
| Thickener2 | The Thickener 2 model is mainly used in the Dynamic mode to separate solids from the liquids in the feed stream. The unit can be configured to have surge, allowing the user to set the underflow rate. Alternatively, the model can calculate the required underflow rate to give the user defined underflow solids fraction. The user may add Reactions, Makeups, EHX and Evaporation to the model. |
Other General Models
There are a number of other general models that may be used in a project. All models are available with a standard Steady State or Dynamic license.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Makeup Source | A source of material, used together with a Makeup Block (MU) to add material directly to a unit. |
| Discard Sink | A destination of material, used together with a Discard Block (DB) to remove material directly from a unit. |
| DirectLink | Similar to a simplified pipe, this is used to transfer material between special types of units. DirectLinks are created automatically. |
| Flange | These represent the IO (Input/Output) connections between pipes and units. Flanges exist automatically and have no associated graphics object. |
| Tear | These represent breaks in the model which must be closed as part of model convergence. Tears are created automatically by the solver engine in recycle loops and flash trains. |
| Area Model | Area Model was removed in Build 139. Used in Dynamic to represent an area. Material may flow to an area. Unit models will belong to an area model. |
Control Models
There are a number of models in SysCAD that are used for process control purposes. The following 3 models are the most common Control models used in both Dynamic and Steady State projects and are available with a standard license.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| General Controller (PGM) | Used to simulate plant control functions and to perform user-defined calculations. This model uses a defined programming convention and allows the users to implement loops, comparison operations, counters, etc. |
| PID Controller | Used to simulate PID controls in the model. This may be used in both dynamic and steady state models. |
| Set Tag Controller | Used for ratio control or setting multiple tags with a common value. |
Control 2 Models
The following Control models are also used for process control purposes and are available with a standard license.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Steady State and Dynamic Process Control Models | |
| Get Tag List | Used to generate a list of values from SysCAD in an external file, often an Excel report. |
| Set Tag List | Used to set predefined values from external sources, usually Excel, into a SysCAD model. |
| Slew Rate Controller | Used to gradually change a process variable to a setpoint. |
| Scheduled Task | Used to execute commands / tasks at scheduled times. |
| Actuator | Mainly used to add visibility to process instrumentation for control schemes. |
| Transmitter | Mainly used to add visibility to process instrumentation for control schemes. |
|
Dynamic Only Process Control Models | |
| Downtime | Used to simulate downtime of a piece of equipment due to a regular event (such as maintenance) and/or failure or other causes. |
| Events | Used to read in timed process variable changes. Data is presented in a table with single variable change against a single time column. Events do not need to be sorted by time. |
| Noise Controller | Allows the user to add disturbance to a dynamic model. |
| Signal Waveform | Allows the user to add waveform type of variation to process variables. |
| Profile | The profile model reads a data file of numbers for increasing times into the model. This is used in dynamic models to adjust variables with time, such as reliability data for equipment, rainfall figures for a year, etc. |
| Queue Profile | Used to read in process variable changes based on a trigger command. |
| Flash Train Control | Used to help balance the pressure for flash train units, currently only works for flash trains involving Flash Tank2 and Shell and Tube heat exchanger 2 |
| Scheduled Events | Can be used to simulate periodic events in a plant model, such as Batch Addition, Reagent dosing, Batch Filtration, etc. The model allows a tag to be set to one of two values depending on whether the unit is active or inactive due to a scheduled event. |
Statistical Models
All statistical models are available with a standard Dynamic license.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Bivariate Statistics | Calculates and displays statistics for two variables and their correlation. |
| Flow Statistics | Generates statistics for flow variables. Eg, production rate |
| General Statistics | Allows the user to collect statistical information for selected variables for a dynamic simulation, e.g tank levels, flows through pipes, etc. |
| Single Variable Histogram | Calculates and displays statistics for a single variable. |
Size Distribution Models
These models are used in projects that contain and require the tracking and manipulation of particle size data (PSD). The models manipulate the material based on the size distribution information. All models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license. While the Size Distribution add-on is not required to be able to insert these models into a project, it is required if the user wishes to use any of the PSD methods within the models. Some models require an additional add-on as shown in the table below.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Size Distribution Definition | The size distribution data for the feed material must be defined. This is done via the Feeder-Cross Page Connector |
| Crusher2 | The model handles multiple ores with common or different parameters. Some of the methods calculate the power required. The user can select any of the following methods:
|
| Hydrocyclone | The hydrocyclone model replaces the old cyclone model. It allows the user to select any of the following methods:
|
| Screen 2 | The Screen 2 model replaces the old Screen model. Multi-layer Screen model with maximum of 8 separation decks. Separation methods include:
|
| Change Sieve Series | This module is used to change from one sieve size to another. |
| The following sub-model/model does NOT require PSD to operate, but does contain PSD as an optional method. | |
| Flotation Cell | User can specify the recovery based on size data. See Recovery for more information. |
| Precipitator3 | The precipitator 3 model is used in the Alumina industry and requires the Alumina add-on.
|
| Solid-Liquid Separator | The Solid-Liquid Separator sub-model is used in the General Separator, Evaporator and Precipitation3 models. It allows splits between two outlets based on size data. See Solid Separation for more information. |
| Solids Recovery Unit | User can specify the recovery based on size data. Size recovery can be applied to the concentrate and/or the middling stream. See Recovery for more information. |
| The following are legacy models, will be removed in future updates. | |
| Crusher | This model will be replaced by the Crusher2 model. User should change the model to the Crusher2. |
| Mill | This model will be replaced by the Crusher2 model. User should change the model to the Crusher2. |
Met Dynamics Models
Available from Build 139.35544.
These specialised PSD models are used in projects that contain and require the tracking and manipulation of particle size data (PSD).
The Size Distribution, Integrated Libraries and Met Dynamics SysCAD add-ons are required to be able to use these models in a project. A Met Dynamics Models license is also required from Met Dynamics to be able to use these models in SysCAD.
Refer to Met Dynamics Overview.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Met Dynamics - Classifier | This model allows the user to model a Classifier using size distributions to determine solid splits between overflow and underflow streams. The user can select any of the following methods:
|
| Met Dynamics - Crusher | This model handles multiple ores with common or different parameters. The user can select one of the following methods:
|
| Met Dynamics - Dense Medium Separator | This model allows the user to model a Dense Medium Separator using size distributions and/or density to determine solid splits between floats and sinks streams. The user can select any of the following methods:
|
| Met Dynamics - Flotation | This model allows the user to model a flotation cell using size distributions to determine solid splits between concentrate and tailings streams. The user can select one of the following methods:
|
| Met Dynamics - Gravity Concentrator | This model allows the user to model a Gravity Concentrator using size distributions and/or density to determine solid splits between concentrate and tail streams. The user can select any of the following methods:
|
| Met Dynamics - HPGR | The High Pressure Grinding Rolls (HPGR) model can handle multiple ores with common or different parameters. The user can select any of the following methods:
|
| Met Dynamics - Hydrocyclone | The Hydrocyclone model allows the user to select any of the following methods:
|
| Met Dynamics - Magnetic Separator | Available from Build 139.36389. The Magnetic Separator model is designed to separate solids based on their magnetic properties. |
| Met Dynamics - Mill | The Mill model can handle multiple ores with common or different parameters. The user can select any of the following methods:
|
| Met Dynamics - Pump | Used in dynamic projects with Transfer mode and in Steady State projects. Simulates a centrifugal slurry pump. |
| Met Dynamics - Screen | A multi-layer Screen model with maximum of 8 separation decks. Separation methods include:
|
Pressure Changing Models
In SysCAD Steady State the stream pressure are usually managed by setting the operating pressures in some of the unit models. However the valve and pump models are also used for setting pressure drops and boosts, especially in vapour lines. All models are available with a standard license.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Steady State and Dynamic Pressure Changing Models | |
| Compressor | Gas compressor used to increase the pressure of gas streams. |
| Gas Pump | Used in dynamic projects with Transfer mode and in Steady State projects. It serves as a simple pressure boost model. |
| Non Return Valve | Used in dynamic projects with Transfer mode and in Steady State projects. It serves as a simple pressure drop model. In this mode, the flow through the pump is specified in the upstream pipe or in the feeder connected to the pump. |
| Pressure Exchanger | Used to model energy recovery devices such as those used in reverse osmosis plants to recover energy from high pressure brine streams. The pressure energy in a high pressure feed is transferred to a low pressure stream, thus acting like a pump for the low pressure stream, increasing its pressure. |
| Pump 1 | Used in dynamic projects with Transfer mode and in Steady State projects. It serves as a simple pressure boost model. In this mode, the flow through the pump is specified in the upstream pipe or in the feeder connected to the pump. |
| Pump 2 | Used in dynamic projects with Transfer mode and in Steady State projects. It allows users to set the pump speed or the pressure boost. The pump will NOT control the flow, but the user can use the pressure boost results to set the flow through the piping system. |
| Reducer | Used to change to a smaller pipe size. In steady state projects, it serves as a pressure-changing model. |
| Valve 1 | Used in dynamic projects with Transfer mode and in Steady State projects. It serves as a simple pressure drop model. In this mode, the flow through the valve is specified in the upstream pipe or in the feeder connected to the valve. |
| Valve 2 | Used in dynamic projects with Transfer mode and in Steady State projects. It allows users to set the valve opening and calculates the pressure drop due to flow. The valve will NOT control the flow, but the user can use the pressure drop results to set the flow through the piping system. |
|
Dynamic Only Pressure Changing Models | |
| Pump 1 - Dynamic Transfer Pull | Used in dynamic projects with Transfer Pull Flow Calculation mode. It allows the user to set pump capacity and speed. In this mode, the maximum flow through the pump can be specified inside the pump model. |
| Valve 1 - Dynamic Transfer Pull | Used in dynamic projects with Transfer Pull Flow Calculation mode. It allows the user to set valve capacity and opening position. In this mode, the maximum flow through the valve can be specified inside the valve model |
| Piping System Model | Mainly used in dynamic projects with Transfer mode. It consists of a number of sub-units, which together comprise a 'Piping System'. The user specifies which sub-units will comprise the piping system and configures them so that they comprise the total piping system. The piping system model then calculates the pressure drop across each sub-unit and hence across the entire system. |
Material Handling Models
These are dynamic only models used for material handling. When these models are in use, the pipes connected to the unit operation will operate in transfer mode. All models are available with a standard Dynamic license.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Conveyor Belt | A model with surge capacity, speed and a number of take-off and feed points as well as drives with moving positions. The material on this unit moves along the belt in discrete packages, to emulate a true belt conveyor. |
| Multi-Storage | A model for multiple parallel bins or stockpiles. |
| Tailings Dam | A model for a dam with two layers, a solids bed and a clarified liquor layer. |
| Material Body | Available from Build 139. This unit operation can be used to simulate the transfer of heat through a body of material. Examples of this are linings of kilns or smelters, and insulation of vessels and pipes. |
| Heap Leach | Available from Build 139.32925. The purpose of the heap leach unit is to dynamically simulate the behaviour of a layered bed of solids reacting with a liquid solution added to the top of the bed. It can be used to simulate heap leach operations, where the bed of solids is ore, or a column such as an ion exchange column. |
Sub-Models
There is a range of different sub-models included in SysCAD. These sub-models are available in many different unit operations models. Depending on the individual unit operation model, some of the sub-models are available as options that may be switched on or off by the user and other sub-models are included automatically. Once a sub-model has been enabled, the access window for that sub-model becomes visible on a tab in the main unit operation's access window. The sub-models generally need to be configured for the desired behavior via the access window.
Note that not all sub-models are available in all unit operations. Many of the Sub-Models are available through Evaluation Blocks which provide an easy way to control which sub-models are enabled and in what order they are evaluated.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Sub-Model Evaluation Sequence | User may enable multiple sub-models within a unit operation. If more than one sub-models are enabled, then each sub-model will be evaluated in sequential order. The evaluation sequence will show the order. User may change the order if required. |
| Local Solubility (PC) | The "Solubility.On" sub-model is only visible if solubility data has been defined in the Species Database. |
| Local Phase Change @ T | The "[email protected]" sub-model is only visible if (1) phase change at temperature data has been defined in the Species Database (2) the global Phase Change @ T function Plant Model - Species tab page is not enabled. |
| Makeup Block (MU) | This gives the user a number of flexible controlled methods to add material to the model from a Makeup Source without connecting and configuring a normal stream. |
| Reaction Block (RB) | The reaction block allows the user to add reactions to most of the main models. The user creates a text file containing the reactions using the designated reaction editor. The reactions are then read into the model. |
| Heat Exchanger - Tank (HX) | The HX Sub model is used in the Tank model. This allows a heat exchange between a stream (heating or cooling fluid) and the contents of a tank. Used for sensible heat exchange only, no condensation or evaporation allowed in the heating or cooling media. |
| Heat Exchanger - Evaporator (HX) | The Embedded Heat Exchanger is used in the Evaporator models. It allows heating or cooling of Evaporator contents with external media (heating or cooling fluid). |
| Environmental Heat Exchange (EHX) | This allows the user to enable heat transfer between the environment and the unit operation. There are a number of different options for specifying heat exchange with the environment. |
| Evaporation Block (Evap) | It allows the user to specify evaporation from the unit via a number of methods. |
| Vapour Liquid Equilibrium (VLE) | This allows the user to select the vapour: liquid equilibrium behaviour of the material in the unit. |
| Discard Block (DB) | Similar to makeup block, this gives the user a number of flexible controlled methods to remove material from the model to a Discard Sink without connecting and configuring a normal stream. |
| Split Flows (Split) | This gives the user a large amount of flexibility in determining the flow of material from the unit. The user may split the flow between two or more exiting streams based on percentage of total flow, phase, species, or any combination. |
| Split Thermal (SplitT) | This gives the user the flexibility to specify outlet stream temperatures, if they need to be different. The overall heat is conserved. |
| Solid-Liquid Separator | The Solid-Liquid Separator block allows the user specify the solid/liquid split between 2 outlet streams. This sub-model allows the user flexibility when setting the splits. |
| Material | Available from Build 139. The Material sub-model is used to simulate the transfer of heat through a body of material. It is used in the Material Body model. |
| Model Procedure (MP) | The model procedures can be switched on for the Tank, Tie and Pipe unit models. It allows user to add in extra functionality for the unit model, such as user-defined calculation methods or correlations. Please see Model Procedures and MP Example Files for more information. |
Qualities Models
Quality Models are used to further define stream data or a species model for use in stream or unit operations. These are usually optionally created for different sections of the flowsheet. See Qualities Models for a general description of how to use qualities models. All models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license. Some models require an additional add-on as shown in the table below.
| Name | Description | Required Add-On |
|---|---|---|
| LockUp | The user may hide a percentage of one or more species from any reactions in the flowsheet. For example, in a gold plant, there may be 10% of the gold that cannot be recovered. This could be Locked up by the user and will never be recovered in the model. | |
| Material Tracking | This option is used to 'track' one or more species in a project, e.g. if the user has different feed sources to a plant, they can track these sources and SysCAD will then show how much of each product is attributable to each source of material. | |
| Size Distribution (PSD) | The user selects the size intervals of interest and defines which species do have size characteristics. | Size Distribution |
| Specific Surface Area (SSA) | Single value representation of size distribution. Commonly used in precipitation in Alumina models. |
Species Models
The species model selected by the user determines all properties of the streams or unit contents within a flowsheet. Examples of properties are Density, Specific Heat, etc.
The default species model to be used is defined in the project configuration file. Normally this is the Standard Species Model whose properties or generally based on the Mass Weighted Mean of the components. The properties of the individual species are taken from the species database (SysCAD.93.db3). This database is compiled by the user and must be checked to ensure data used are correct. For help on the entering and modifying data in the SysCAD.93.db3 file, please see Species Table.
In addition to the Standard species model, which is available to all SysCAD users, other client specific species models may be developed for a specific project or client. For example, in the Aluminium industry, the generic Bayer properties model is adapted for specific refineries.
Changing Species Models describes how a species model is selected.
Species models are available in Steady State and Dynamic with the appropriate add-on license, as shown in the table below.
| Name | Description | Required Add-On |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | This is the default species model used by SysCAD. Most physical and thermodynamic properties are calculated on a simple mass weighted mean basis. | |
| Bayer3 | Uses NaAl[OH]4(aq) as Alumina and Al[OH]3(s) as Gibbsite. Used with Alumina unit models. | Alumina |
| Potash | Equations used are based on published work by Laliberté et al. Requires KCl(aq), KCl(s), NaCl(aq) and NaCl(s) as valid species in the project. Used with Potash unit models. | Potash |
| Sugar | Uses C12H22O11(aq) as soluble Sugar and C12H22O11(am) / C12H22O11(xt) as crystalline Sugar. Used with Sugar unit models. | Sugar |
Alumina Models
Alumina models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license with the Alumina add-on. These models are developed especially for the use in the Alumina industry and must be used with a Bayer Stream Properties model.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Alumina 3 Bayer Species Model | Calculates the properties of the streams based on Bayer3 liquor properties. Uses NaAl[OH]4(aq) as Aluminate; Al[OH]3(s) as Gibbsite; AlO.OH(s) as Boehmite and Na2SiO3(aq) as dissolved sillica. |
| Alumina 3 Bayer Equations | Lists the equations used by the Alumina 3 Bayer Species Model. |
| Precipitation 3 Model | The model is for use in the alumina industry only. NOTE that this model requires NaAl[OH]4(aq) as Aluminate and Al[OH]3(s) as Gibbsite, therefore requires Bayer3 Species Model. This model can also operates in Dynamic with additional functionality. |
| General Bayer Data | General information about the alumina Bayer properties models. Used in the alumina industry only. |
| Heat of Dissolution of Gibbsite and Boehmite | The Heat of Dissolution of Gibbsite and Boehmite in Bayer Liquors in SysCAD reactions. Detailed papers on the Heat of Dissolution of Gibbsite and the Heat of Dissolution of Boehmite can be downloaded from http://www.syscad.net/downloads. |
Potash Models
Potash models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license with the Potash add-on. These models are developed especially for the use in the MOP (Muriate of Potash) industry and must be used with a Potash Stream Properties model.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Potash Species Model | Calculates the properties of the streams based on potash liquor properties. |
| Potash Solubility | The implemented Potash Solubility information are documented here. |
| Potash Evaporator | Achieves vapour liquid equilibrium for a defined set of conditions and allows the user to enable Reactions and/or Solubility to produce salt crystals that can be washed in the Evaporator 'Leg'. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
Sugar Models
Sugar models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license with the Sugar add-on. These models are developed especially for the use in the Sugar industry and must be used with a Sugar Stream Properties model.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Sugar Species Model | Calculates the properties of the streams based on sugar liquor properties. |
| Sugar Cane Shredder | The sugar Cane Shredder is used to prepare sugar cane by opening plant cells to allow the release of juice before it goes to the crushing operations. |
| Sugar Crusher | This model is used to squeeze and separate juice from a shredded cane feed. The model is for use in the sugar industry only. |
| Sugar Crystalliser | The sugar crystallizer is used to precipitate aqueous sugar from molasses onto existing sugar crystals. |
| Sugar Dryer | The sugar dryer is a counterflow dryer used to cool and dry sugar crystals in the final stage of processing. |
| Sugar Fugal | This model is used to centrifuge and wash sucrose crystal. The model is for use in the sugar industry only. |
| Sugar Fugal 2 | This model is used to centrifuge and wash sucrose crystal. The model is for use in the sugar industry only. |
| Sugar Juice Screen | The sugar juice screen is used to separate mud solids and fibre from juice expressed during crushing operations. |
| Sugar Mud Filter | The mud filter is used to wash juice from mud solids before it leaves the process. |
| Sugar Vacuum Pan | The sugar vacuum pan is used to precipitate aqueous sugar onto existing sugar crystals in a continuous operation (as opposed to batch operation). |
| Falling Film Evaporator 3 | The Falling Film Evaporator 3 (FFE3) unit operation is used to model evaporation of water from juice. The model works for both falling and rising film evaporators (such as a Roberts evaporator). |
Thermodynamic Calculation Engines
These models use a seamless link to third-party Thermodynamic Calculation Engines (TCEs) to provide rigorous solution chemistry calculations. The engines include ChemApp (which can use database files exported from FactSage), OLI, PHREEQC, and AQSol.
NEW from August 2022: ALL TCE options are now included under a single TCE license add-on without the requirement to purchase separate SysCAD add-ons for OLI / PHREEQC / ChemApp or AQSol. Customers with an existing OLI add-on, PHREEQC add-on, ChemApp add-on or AQSol add-on will be entitled to use any of these options in Build 139 from September 2022.
TCE Overview and Common Functionality
The following are relevant for all Thermodynamic Calculation Engine (TCE) models.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermodynamic Calculation Engines | A summary description of the TCE capability. |
| TCE Functionality Overview | Describes the workflow for using TCE models in a SysCAD Model, user functionality and solver multithreading. |
| TCE Species Mapping | Describes species mapping in forward and reverse directions. |
| TCE Configuration Options | Describes the options which can be configured in the Project Configuration (cfg) file. (Available from Build 139.29706.) For earlier versions of SysCAD, user may need to edit the configuration file manually. See TCE Configuration Options for more information. |
AQSol Models
Available from Build 139.30140.
AQSol models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license with the TCE Add-On (or formerly purchased AQSol Add-On). The AQSol program can be used for general phase equilibrium calculations and process simulations for aqueous solutions.
- The AQSol software is developed and maintained by Aqueous Solutions ApS, Søborg, Denmark, (refer to www.phasediagram.dk for further information).
- It is assumed that the user has some familiarity with the theory and use of the AQSol program.
- AQSol is used in a flexible way in Unit or Control models at appropriate locations in a plant model. It is not implemented as a Species Properties Model.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| AQSol Overview | Brief introduction of the option and project workflow overview of how to use the option in SysCAD. |
| AQSol Model Configuration | Used to define and view various options for the selected AQSol database, including management of mapping of SysCAD species list to species list used in AQSol. |
| AQSol Direct Calc | Stand alone unit model to perform side calculations using AQSol for predicting aqueous chemistry equilibrium conditions and properties on a user defined AQSol stream. |
| AQSol Side Calc | Stand alone unit model to perform side calculations using AQSol for predicting aqueous chemistry equilibrium conditions and properties on a SysCAD stream in the current project. The model has the ability to combine several streams/contents to be evaluated by a single Side Calc model. |
| AQSol Reactor | Include this model in a SysCAD stream to use AQSol to calculate predicted outlet conditions. |
| AQSol Evaporator | Available from Build 139. Uses AQSol to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. May be used as a Crystallizer. Allows embedded HX and slurry separator. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| AQSol Flash Tank | Available from Build 139. Uses AQSol to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. May be used as a Crystallizer. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| AQSol Reverse Osmosis | Available from Build 139. Uses AQSol to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. The user may specify the yield and efficiency of the process, as well as the outlet pressure requirements. |
| AQSol Feeder | Available from Build 139.30807. Uses AQSol to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties of a specified feed. |
ChemApp Models
Available from Build 139.
ChemApp models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license with the TCE Add-On (or formerly purchased ChemApp Add-On). ChemApp is a computer program for thermodynamic phase equilibrium calculations. It can use database files (CST files) generated using the FactSage family of products.
- It permits the calculation of complex, multicomponent, multiphase chemical equilibria and their associated extensive property balances.
- ChemApp gtt-technologies.de/software/chemapp is developed and maintained by GTT-Technologies gtt-technologies.de.
- FactSage www.factsage.com is by CRCT ThermFact Inc www.crct.polymtl.ca/index.html and GTT-Technologies gtt-technologies.de.
- It is assumed that the user has some familiarity with the theory and use of the ChemApp and/or FactSage program.
- ChemApp is used in a flexible way in Unit or Control models at appropriate locations in a plant model. It is not implemented as a Species Properties Model.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ChemApp Overview | Brief introduction of the option and project workflow overview of how to use the option in SysCAD. |
| ChemApp Model Configuration | Used to define and load the required ChemApp Model Definition file (ChemApp species data), and for mapping of species between ChemApp and SysCAD, so that SysCAD streams can be converted to ChemApp input and vice versa. |
| ChemApp Direct Calc | Stand alone unit model to perform side calculations using ChemApp for predicting chemistry equilibrium conditions and properties on a user defined ChemApp stream. This model does not require species mapping between ChemApp and SysCAD. Input and output are entered and displayed using ChemApp species. |
| ChemApp Side Calc | Stand alone unit model to perform side calculations using ChemApp for predicting chemistry equilibrium conditions and properties including on a SysCAD stream in the current project. This model requires species mapping, the specified SysCAD stream information is converted into ChemApp input, and the resulting ChemApp output is displayed using ChemApp species. The model has the ability to combine several streams/contents to be evaluated by a single Side Calc model. |
| ChemApp Reactor | Include this model in a SysCAD stream to use ChemApp to calculate predicted outlet conditions. This model requires species mapping, the inlet SysCAD stream information is converted into ChemApp input, and the resulting ChemApp output is converted back to SysCAD species (if using the reactor calculation mode). |
| ChemApp Feeder | Available from Build 139.30807. Uses ChemApp to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties of a specified feed. |
| ChemApp Tank | BETA version available from Build 139.36061. Uses ChemApp to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties of a tank with surge. For Dynamic projects only. |
PHREEQC Models
Available from Build 139.
PHREEQC models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license with the TCE Add-On (or formerly purchased PHREEQC Add-On). PHREEQC is a computer program that is designed to perform a wide variety of aqueous geochemical calculations.
- It is developed and maintained by the United States Geological Survey. (refer to https://www.usgs.gov/software/phreeqc-version-3 for further information)
- It is assumed that the user has some familiarity with the theory and use of the PHREEQC program. It is recommended that PHREEQC is installed.
- PHREEQC is used in a flexible way in Unit or Control models at appropriate locations in a plant model. It is not implemented as a Species Properties Model.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PHREEQC Overview | Brief introduction of the option and project workflow overview of how to use the option in SysCAD. |
| PHREEQC Model Configuration | Used to define and view various options for the selected PHREEQC database, including management of mapping of SysCAD species list to species list used in PHREEQC. |
| PHREEQC Direct Calc | Stand alone unit model to perform side calculations using PHREEQC for predicting aqueous chemistry equilibrium conditions and properties including pH on a user defined PHREEQC stream. |
| PHREEQC Side Calc | Stand alone unit model to perform side calculations using PHREEQC for predicting aqueous chemistry equilibrium conditions and properties including pH on a SysCAD stream in the current project. The model has the ability to combine several streams/contents to be evaluated by a single Side Calc model. |
| PHREEQC Reactor | Include this model in a SysCAD stream to use PHREEQC to calculate predicted outlet conditions. |
| PHREEQC Evaporator | Available from Build 139. Uses PHREEQC to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. May be used as a Crystallizer. Allows embedded HX and slurry separator. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| PHREEQC Flash Tank | Available from Build 139. Uses PHREEQC to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. May be used as a Crystallizer. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| PHREEQC Reverse Osmosis | Available from Build 139. Uses PHREEQC to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. The user may specify the yield and efficiency of the process, as well as the outlet pressure requirements. |
| PHREEQC Solvent Extraction | Available from Build 139. Uses PHREEQC to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. The Solvent Extraction unit will mix perfectly all the input streams, complete species transfer across phases, then separate the output based on individual phase or density. |
| PHREEQC Feeder | Available from Build 139.30807. Uses PHREEQC to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties of a specified feed. |
| PHREEQC Pond | BETA version available from Build 139.30599. Uses PHREEQC to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties of a pond with surge. For Dynamic projects only. |
| PHREEQC Tank | BETA version available from Build 139.36061. Uses PHREEQC to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties of a tank with surge. For Dynamic projects only. |
OLI Models
OLI models are available with a Steady State or Dynamic license with the TCE Add-On (or formerly purchased OLI Add-On). An appropriate OLI license from OLI Systems (olisystems.com) is required. OLI in SysCAD is not implemented as a Species Properties Model but as a unit model for use at appropriate locations in a plant model. These models use OLI Systems leading Electrolyte Simulation Software to predicate equilibrium conditions and properties (such as pH) for aqueous chemistry.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| OLI Overview | Brief introduction of the option and project workflow overview of how to use OLI in SysCAD. |
| OLI Model Configuration | Available from Build 139.31848. Used to define and view various options for the selected OLI database, including management of mapping of SysCAD species list to species list used in OLI. |
| OLI Direct Calc | Available from Build 139.31848. Standalone unit model to perform side calculations using OLI for predicting aqueous chemistry equilibrium conditions and properties including pH on a user defined OLI stream. |
| OLI Side Calc | Available from Build 139.31848. Standalone unit model to perform side calculations using OLI for predicting aqueous chemistry equilibrium conditions and properties including pH on a SysCAD stream in the current project. The model has the ability to combine several streams/contents to be evaluated by a single Side Calc model. |
| OLI Reactor 2 | Available from Build 139.31848. Include this model in a SysCAD stream to use OLI to calculate predicted outlet conditions. |
| OLI Evaporator | Available from Build 139.31848. Uses OLI to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. May be used as a Crystallizer. Allows embedded HX and slurry separator. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| OLI Flash Tank | Available from Build 139.31848. Uses OLI to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. May be used as a Crystallizer. Can be used as part of a Flash Train. |
| OLI Reverse Osmosis | Available from Build 139.31848. Uses OLI to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. The user may specify the yield and efficiency of the process, as well as the outlet pressure requirements. |
| OLI Solvent Extraction | BETA version available from Build 139.34985. Uses OLI to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties. The Solvent Extraction unit will mix perfectly all the input streams, complete species transfer across phases, then separate the output based on individual phase or density. |
| OLI Feeder | Available from Build 139.31848. Uses OLI to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties of a specified feed. |
| OLI Pond | BETA version available from Build 139.34246. Uses OLI to calculate the equilibrium conditions and properties of a pond with surge. For Dynamic projects only. |
Legacy Models
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| OLI Chemistry Model | Define and view various options for the selected OLI chemistry model, including management of mapping of SysCAD species list to species list used in OLI. |
| OLI Sample Model | Stand alone unit model to perform side calculations using OLI for predicting aqueous chemistry equilibrium conditions and properties including pH. |
| OLI Reactor | Flexible general purpose unit model using OLI software to calculate product stream composition and properties based on user options and feed. Functionality is similar to SysCAD Reaction Block and FEM where for a given feed, reactions occur with optional heat exchange. |
Common Sections
There are many tab pages or groups of tags that are common to all or many models.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Common Content Section | Feed flow properties and species compositions, usually for setting of flow and makeup in models such as Feeders and Makeup Sources. This can also be the preset image used to set the tank contents in dynamic projects.
|
| Material Content Section | Material Content section, mixture properties and species compositions of material in the content. For Example: Container mass, usually for dynamic units with surge, such as tank or thickener.
|
| Material Flow Section | Material flow section, listing flow properties and species compositions of material flow. Usually for pipes, flow in or out of model, etc.
|
| Info | General sections on first and Info tab pages for all models. |
| Links | Summary tables for all the input and output links. |
| Audit | Summary of mass and energy balance (inputs/outputs) of a model. |
System Models
There are a number of system "models" that are used in a project.
Environmental Models
The new Seawater/Brine models provide accurate thermophysical properties for seawater and concentrated brines, based on the IAPWS 2008 model
The International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam, Berlin, Germany, Release on the IAPWS Formulation 2008 for the Thermodynamic Properties of Seawater
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Seawater Species Model | Accurate seawater thermophysical properties. |
Examples
General Description
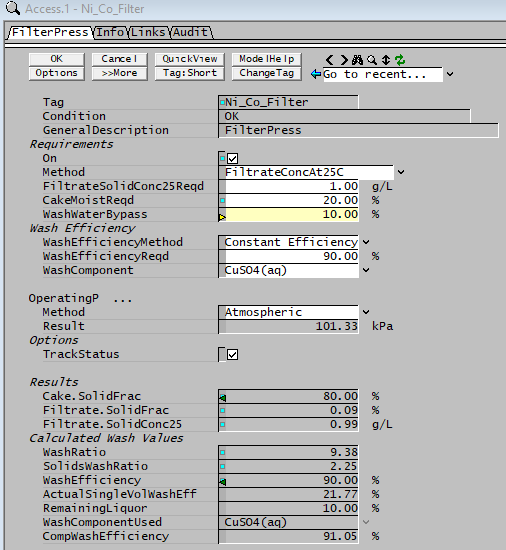
Each model (unit or link), has a properties or access window, which the user can view by right clicking on the unit. The access window differs for each model. However, they all show the variables associated with that particular model. These variables fall into two main categories:
- Variables those are required to define the model.
- These variables are inputs to the model and are displayed on a white background. For example in the access window below, user is required to define the variables:
- FiltrateSolidFracReqd / FiltrateSolidConc25Reqd, CakeMoistReqd and WashWaterBypass.
- The filter model uses these settings to calculate the material split from the unit.
- Variables with a yellow background means the variable is being set by a controller. See Access Field Reference Tag Status Colour for more information.
- Variables those are calculated by the model.
- These variables are displayed on a grey background and cannot be changed by the user.
- In the access window below, the model calculates Cake.SolidFrac and Filtrate.SolidFrac and so on.
The access window may consist of more than one section. For example, the FilterPress shown above consists of four sections: -FilterPress-, Info, -Links- and -Audit- (If a tab marked ... is present, it indicates that it is a continuation from the previous section.)
The user can view each of these sections by clicking on their respective tab at the top of the page. The variables for that section can then be accessed.
This document attempts to describe each model, or process unit, for the user. The documentation for each model has the following format:
- General Description
This briefly outlines the purpose of the unit and how it operates within a flowsheet. - Diagram (if applicable)
This shows the default drawing of the unit with the appropriate stream connected to the unit. - Inputs and Outputs (if applicable)
This section lists all the streams that can be connected to the unit. It also gives the essential connections, without which the unit cannot operate, and the number of streams that can be connected to each connection. - Model Theory
The method by which the unit calculates the material split. Any equations used to define the unit are given in this section. - Data Sections
This attempts to quantify the variables for each unit-s access window.