Solvent Extraction Unit
Navigation: Models ➔ Mass Separation Models ➔ Solvent Extraction Unit
This page is for SysCAD 139 and later. For Build 138, please see Solvent Extraction Unit 138.
General Description
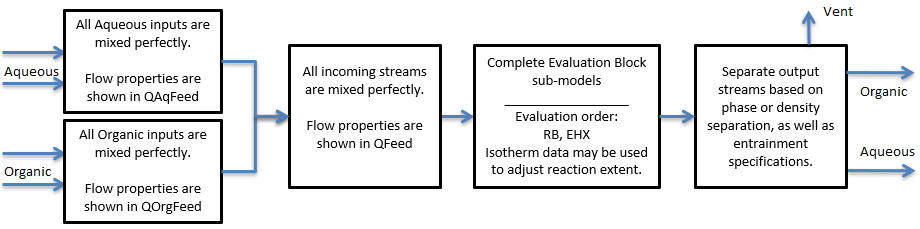
The Solvent Extraction unit will mix perfectly all the input streams, complete species transfer across phases, then separate the output based on individual phase or density.
User can set up the unit for solvent extraction or organic stripping. The model also allows imperfect separation of products, to do this, specify aqueous entrainment in organic and/or organic entrainment in aqueous.
Defining species
User is responsible for setting up a suite of species which accurately portrays the application that is being evaluated. As the separation of the mixture will be based on individual phase or density, we recommend defining all aqueous species with individual phase (aq) and all organic species with individual phase (o). If using separation by density, please ensure the organic species are defined with a lower density than the aqueous species.
Some example species are listed below:
- Aqueous species (aq): H2O, H2SO4, CuSO4, FeSO4, Fe2[SO4]3
- organic species (o): Kerosene, RH, R2Cu, R2Fe, R3Fe.
- This suite of species is typically set up for chelating type of organic solvents such as the LIX hydroxy oxime copper extractants available from the Henkel Corporation i.e. LIX 64N, 65N, 860, 864, 865, and 622.
Species transfer across phases
The transfer of the species across phases (Aqueous->Organic OR Organic->Aqueous) can be specified via the reaction block.
- For example, for extraction of Cu from the aqueous into the organic phase, we can use the following reaction:
- 2RH(o) + CuSO4(aq) = R2Cu(o) + H2SO4(aq)
- Or, in the case of stripping of Cu from the organic phase back into the aqueous phase, we can use the following reaction:
- R2Cu(o) + H2SO4(aq) = 2RH(o) + CuSO4(aq)
The extent of the reaction be either be a user specified value or by reading from the McCabe Thiele diagram isotherms.
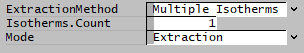
- To specify the reaction extent directly in the reaction, set the ExtractionMethod = 'None',
- To define and read values from a McCabe Thiele diagram, ExtractionMethod = 'Multiple Isotherms'. (Multiple Isotherms is the new method available in SysCAD 139 to allow multiple isotherms)
NOTES (Isotherm Method):
- The Isotherm2 method is retained for backward compatibility purposes. This is identical to using the Multiple Isotherms method with Isotherms.Count = 1.
- By selecting the "AllowOverride" option for the IsoTherm, it can be used as a "side calculation" displaying required reaction extent and user can set the reaction extent used.
- Please see model theory for more detail on how to use the isotherm feature.
Phase Separation
The user may choose to separate the mixture based on either Individual Phase or density:
- IndPhase to Organic: The user specifies the Individual phase that will report to the Organic stream.
- Note: All solids and other liquid phases will classed as Aqueous.
- Density: The user specifies the density of separation. In this case the aqueous species are normally denser than the user defined density of separation and the organic species are less dense. e.g. with a separating density of 950 kg/m3, water and all dissolved aqueous species will report to the aqueous phase and the organic species, normally with densities less than approximately 850 kg/m3, will report to the organic phase.
- Note: Solids will also split on density.
Entrainment
The user may also specify the entrainment of the two different liquids:
- Aqueous in the Organic stream. Note this will also include any solids that are in the aqueous phase; and
- Organic in the Aqueous stream.
Heat Loss
User may specify heat loss to the environment by switching on the EnvironHX option. This heat loss will occur after reactions have been completed.
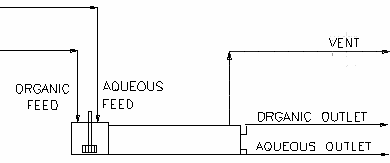
Diagram
The diagram shows the default drawing of the Solvent Extraction unit, with all of the streams that have to be connected for the unit to operate.
The physical location of the streams connecting to the Solvent Extraction unit is unimportant. The user may connect the streams to any position on the unit.
Inputs and Outputs
Label Required
OptionalInput
OutputNumber of Connections Description Min Max Aqueous Inlet 1 Required In 1 20 Aqueous feed to Solvent Extraction unit. Organic Inlet 1 Required In 1 20 Organic feed to Solvent Extraction unit. Aqueous Outlet Required Out 1 1 Aqueous outlet from Solvent Extraction unit. Organic Outlet Required Out 1 1 Organic outlet from Solvent Extraction unit. Vent Optional Out 0 1 Vent Stream. (Vapour Only)
Behaviour when Model is OFF
If the user disables the unit, by un-ticking the On tick box, then the following actions occur:
- All streams connected to the 'Aqueous' inlet will flow straight out of the 'Aqueous' outlet;
- All streams connected to the 'Organic' inlet will flow straight out of the 'Organic' outlet;
- No reactions will occur.
So basically, the unit will be 'bypassed' without the user having to change any connections.
Model Theory
The “Isotherm” method calculates an explicit solution of the mass balance equations for a single Solvent Extraction stage, subject to the constraint that the resulting concentrations of the Primary Metal in the product stream lie on the Isotherm (Equilibrium Line). When there are “Multiple Isotherms” the equations are solved independently for each Primary Metal and Isotherm specified.
The diagram below illustrates the graphical representation of the unit for a single Primary Metal and Isotherm. Primary Metal in the example is extracted to the Organic Phase.
|
For example:
The following is used in example 1, based on 100% stage efficiency.
|
- The Isotherm is determined from experimental data.
- For extraction, the x axis is the concentration of the primary metal in the aqueous phase and the y axis is the concentration of the primary metal in the organic phase.
- For stripping, the x axis is the concentration of the primary metal in the organic phase and the y axis is the concentration of the primary metal in the aqueous phase.
- A mass balance on the primary metal is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ Q_{T} = C_{F,Aq} Q_{F,Aq} + C_{F,Org} Q_{F,Org} = C_{P,Aq} Q_{P,Aq} + C_{P,Org} Q_{P,Org}}} }[/math]
- Where:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ Q_{T} }} }[/math]: Mass flow rate of the primary metal in the Total feed/product
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ C_{F,Aq} }} }[/math]: Feed elemental concentration in the Aqueous Phase
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ C_{F,Org} }} }[/math]: Feed elemental concentration in the Organic Phase
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ Q_{F,Aq} }} }[/math]: Volumetric flow rate of the Aqueous Phase feed
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ Q_{F,Org} }} }[/math]: Volumetric flow rate of the Organic Phase feed
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ C_{P,Aq} }} }[/math]: Product elemental concentration in the Aqueous Phase
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ C_{P,Org} }} }[/math]: Product elemental concentration in the Organic Phase
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ Q_{P,Aq} }} }[/math]: Volumetric flow rate of the Aqueous Phase product
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ Q_{P,Org} }} }[/math]: Volumetric flow rate of the Organic Phase product
- The Aqueous and Organic Feed streams used in the calculation contain, respectively, only aqueous and organic species. A “pre-mix” step is used to ensure that this is the case, transferring aqueous species in the Organic Feed to the Aqueous Feed and organic species in the Aqueous Feed to the Organic Feed.
- The total flow of the primary metal, [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ Q_{T} }} }[/math], can be calculated from the known feed parameters.
- For Extraction, the above equation can be rearranged as the Mass Balance Constraint for the stage:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ C_{P,Org} + C_{P,Aq} \frac{Q_{P,Aq}}{Q_{P,Org}} = \frac{Q_{T}}{Q_{P,Org}} }} }[/math]
- Again for Extraction, the Isotherm is defined by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ C_{P,Org} = f ( C_{P,Aq} ) }} }[/math]
- If the Product stream volumetric flow rates are known, the above equations can be solved to find product concentrations which lie on the Isotherm and satisfy the Mass Balance Constraint.
- Since changes in Product concentrations result in changes in Product stream volumetric flow rates, an iterative calculation is implemented with Product stream volumetric flow rates initially set equal to feed stream volumetric flow rates. A solution is found for all Isotherms, Product flow rates are recalculated and the calculation continues.
- For Stripping, the equations have the form:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ C_{P,Aq} + C_{P,Org} \frac{Q_{P,Org}}{Q_{P,Aq}} = \frac{Q_{T}}{Q_{P,Aq}} }} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ C_{P,Aq} = f ( C_{P,Org} ) }} }[/math]
NOTES:
- The method described above calculates the same solution that can be determined using the McCabe-Theil method, but is more computationally efficient. Please refer to Solvent Extraction Using McCabe-Theil Method for a comparison.
- The equilibrium line is usually based on elemental concentration. Please see example 1 below on how to read the isotherm data.
- In some cases, the total elemental concentration can not be used directly, for example, Fe can be in the form of Fe2+ and Fe3+. If user only wish to get the Fe2+ concentration and not the total Fe concentration, then "User Calc" should be used. To use this option, user-specified calculations must exist to allow mapping of the aqueous and organic values. Please see example 2 on how to set up user calculations.
- The model is not currently sensitive to pH or temperature. The model assumes that the pH and temperature are correct for the particular equilibrium isotherm.
- User can adjust the stage efficiency to emulate cases where there is insufficient contact time to achieve perfect equilibrium. The stage efficiency reduces the calculated reaction extent by the stage efficiency.
Using Isotherms
SolventExtraction Tab
- Set ExtractionMethod = Multiple Isotherms
- Set Isotherms.Count to required number of isotherms (minimum 1).
- Set Mode to Extraction or Stripping.
Set up the reactions
- The data retrieved from each isotherm will be applied to one selected reaction only, the user must make sure the relevant reaction contains the element of interest.
- For example: [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathrm { CuSO_4(aq) + 2 RH(o) = H_2 SO_4(aq) + R_2 Cu(o)}} }[/math]
- The extent species used to adjust the reaction will need to match the ExtentSpecies field on the ITX page. SysCAD will adjust this species reaction extent using values read from the isotherm diagram.
- Extent:Fraction [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf {\mathrm{ CuSO_4(aq) = 0.5}} }[/math]
- The reaction file may contain other reactions that are set by the user.
Set up the isotherm data
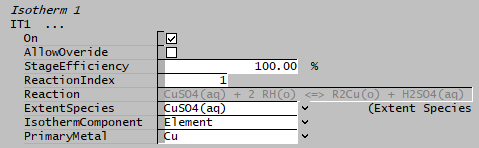
- For each isotherm, on the relevant tab called "ITX" (where X is the isotherm number):
- Set the Stage Efficiency and Reaction Index.
- Set the ExtentSpecies based on the chosen reaction, IsothermComponent and PrimaryMetal.
- Enter the equilibrium curve, specify the number of data points by setting the length.
- Take care to enter the correct concentration in to the correct column: for Extraction it is Aq | Org, for Stripping it is Org | Aq
- The data can also be loaded from or saved to a csv file (comma separated text file).
EXAMPLE 1: Based on total Cu concentration by phase
- Set the IsothermComponent to "Element" and PrimaryMetal to "Cu"
- The Extent Species selected must contain the primary metal element, if not, SysCAD will return an error. (In this example, the extent species for reaction 1 is CuSO4(aq) and the Primary Metal is Cu.)
- All concentration values shown in the Results section will be based on Cu.
- This is the total Cu concentration by phase, so if more than one Cu species is present, the Cu concentration from all species are accounted for.
- The reaction extent of reaction 1 is then adjusted to give the desired concentration.
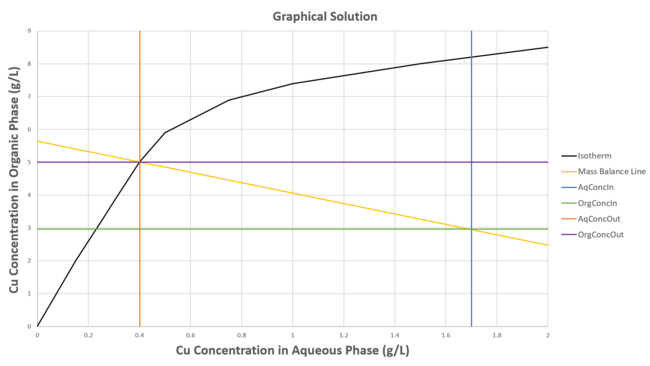
Using the isotherm given in Model Theory, we have:
- Cu concentration in aqueous feed = 1.7 g/L (blue vertical line)
- Cu concentration in organic feed = 2.96 g/L (green horizontal line)
- Based on volumetric feed rates of 9.99 and 6.29 m^3/h for the aqueous and organic feeds, respectively, the total mass flow of Cu is 35.6 kg/h.
- Using the volumetric feed rates (as a first guess) and total mass flow of Cu, the mass balance line (yellow line) can be determined. This estimate can be refined once the final product rates are determined (10.01 and 6.31 m^3/h for the aqueous and organic products, respectively).
- Based on where the mass balance line intercepts the Isotherm line (black line):
- the Copper concentrations in the exiting Aqueous and Organic streams are determined to be Cu(aq) = 0.40 g/L (orange vertical line) and Cu(o) = 5.01 g/L (purple horizontal line), respectively.
The above example assumes a 100% stage efficiency, i.e. perfect equilbrium is achieved. A stage efficiency less than 100% would reduce the calculated reaction extent by the stage efficiency. In the above example, the required extent for the Cu extraction reaction to achieve the target concentration of 5.01 g/L Cu in the organic phase is 76.3%. If the stage efficiency was set to 90%, then the reaction extent would instead be set to 68.7% (76.3*90/100), resulting in Cu concentrations in the exiting Aqueous and Organic streams of Cu(aq) = 0.53 g/L and Cu(o) = 4.81 g/L, respectively.
EXAMPLE 2: Based on User Defined calculations
In some cases, the total elemental concentration may not be used directly, for example, Fe can be in the form of Fe2+ and Fe3+. If user only wish to get the Fe2+ concentration and not the total Fe concentration, then user-specified calculations must be used for mapping of the required aqueous and organic portion, in this example, we will only use Fe2+ while ignoring Fe3+.
- If the user calculations have not been defined yet, please do the following:
- Save and close the project.
- Menu command: Edit | Project Configuration - step 2 of 2 | Calculations:
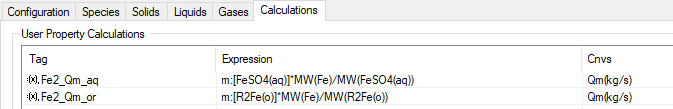
- On the User Property Calculations section (top half), add two user defined properties to represent the required mass flow of the element in the aqueous and the organic phase respectively.
- Examples of these are shown in the following picture, all concentration values shown in the Results section will be based on these calculated mass flow.
- Save the configuration file, reopen the project and resume configuration of the solvent extraction unit.
- Set the IsothermComponent to "User Calcs",
- AqQmUserCalc: select the user property calculation from the drop-list that represents the aqueous mass flow for the required element (e.g. Fe2+ in aqueous phase)
- OrgQmUserCalc: select the user property calculation from the drop-list that represents the organic mass flow for the required element (e.g. Fe2+ in organic phase)
- All concentration values will be based on the user calculations.
- This is NOT the total Fe concentration by phase, so only Fe2+ from FeSO4(aq) or R2Fe(o) is considered.
- The reaction extent of reaction [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathrm { FeSO_4(aq) + 2 RH(o) = R_2 Fe(o) + H_2 SO_4(aq)}} }[/math] is then adjusted to give the desired concentrations.
NOTE:
- This method relies on correctly defined User Property Calculations. Please check the calculations if results do not match expected values.
- The user calculation should be defined in the user property calculation section, not the user species calculation section.
- When using "IsothermComponent" as "User Calcs", the user calculation must refer to the same element or component in both the aqueous and organic phase. In the above example, we have created two user calculations, one for Fe2+ in aqueous phase and another for Fe2+ in organic phase.
Isotherm data and operating condition issues
When using the isotherm data, the user needs to keep in mind that there are a number of conditions where the operating condition may not fall on the isotherm curve:
- Limited by other species that contain the same primary metal - the feed may contain multiple species with the specified Primary Metal. This could cause the metal concentration to be higher than the isotherm data.
- Limited by reactions - Reaction file may contain multiple reactions, but only the chosen reaction (set by the ReactionIndex) is used to adjust the metal concentration, it is possible that even after fully reacting the chosen reaction species, the isotherm concentration cannot be achieved.
- Feed stream concentration too high - operating point falls outside of the isotherm curve.
When operating point is out of range, the concentration will be limited by the isotherm data. A warning message will be displayed, for example:
- "W:Concentration (Y value 10.0555) from operating curve is greater than the maximum specified Isotherm data point. (Max 8.5 used)"
- Extraction - SysCAD will try to satisfy the loaded organic concentration by adjusting the chosen reaction extent. The spent aqueous concentration will be by balance.
- Stripping - SysCAD will try to satisfy the stripped aqueous concentration by adjusting the chosen reaction extent. The organic concentration will be by balance.
- If the reaction extent is being limited (0% to 100%), then it is possible that both the aqueous and organic concentrations will not fall on the isotherm curve.
- When the chosen reaction extent is being limited, the following warning messages will be displayed: "W:RX Extent driven to greater than 100"
See also Further Discussion for more information.
Flowchart
Data Sections
The default access window consists of several sections:
- SolventExtraction tab - Contains general information relating to the unit.
- ITX tab - Optional tab ,or multiple tabs if more than 1 Isotherm is selected. Only visible if one of more Isotherms are enabled.
- RB - Optional tab, only visible if the Reactions are enabled.
- EHX - Optional tab, only visible if the EnvironHX is enabled.
- QAqFeed - Optional tab, only visible if ShowAqQFeed is enabled. This page shows the properties of the mixed aqueous stream, useful when multiple aqueous feed streams are present.
- QOrgFeed - Optional tab, only visible if ShowOrgQFeed is enabled. This page shows the properties of the mixed organic stream, useful when multiple organic feed streams are present.
- QFeed - Optional tab, only visible if ShowQFeed is enabled. This page shows the properties of the mixed stream as the feed to the solvent extraction.
- QAqProd - Available from Build 139. Optional tab, visible if ShowQAqProd is enabled. This and subsequent tab pages, e.g. QAqProd.. and Sp, shows the properties of the aqueous outlet stream. The tags in the QAqProd tab are valid even when the ShowQAqProd option is not selected.
- QOrgProd - Available from Build 139. Optional tab, visible if ShowQOrgProd is enabled. This and subsequent tab pages, e.g. QOrgProd.. and Sp, shows the properties of the organic outlet stream. The tags in the QOrgProd tab are valid even when the ShowQOrgProd option is not selected.
- Info tab - Contains general settings for the unit and allows the user to include documentation about the unit and create Hyperlinks to external documents.
- Links tab, contains a summary table for all the input and output streams.
- Audit tab - Contains summary information required for Mass and Energy balance. See Model Examples for enthalpy calculation Examples.
Solvent Extraction Page
Unit Type: SolventExtraction - The first tab page in the access window will have this name.
| Tag (Long/Short) | Input / Calc | Description/Calculated Variables / Options |
| Tag | Display | This name tag may be modified with the change tag option. |
| Condition | Display | OK if no errors/warnings, otherwise lists errors/warnings. |
| ConditionCount | Display | The current number of errors/warnings. If condition is OK, returns 0. |
| GeneralDescription / GenDesc | Display | This is an automatically generated description for the unit. If the user has entered text in the 'EqpDesc' field on the Info tab (see below), this will be displayed here. If this field is blank, then SysCAD will display the UnitType or SubClass. |
Requirements | ||
| On | Tick box | If this is enabled then the unit will be in full operational mode. If this is disabled, then unit will be 'inoperative', as described in Inoperative Mode. |
| SeparationMethod / SeparMethod | Density | The user selects the Density of Separation. All species (INCLUDING solids) that have a density LESS than this density will report to the organic outlet. All species with a density GREATER than this density will report to the Aqueous outlet. |
| IndPhase to Organic | The user selects the Individual liquid Phase(s) (usually (o)) that reports to the organic phase. All solids and other liquid phases will report to the Aqueous phase. | |
| SeparDensity / SeparRho | Input | Visible if SeparMethod = 'Density'. The required separation density. This must be a value between the density of the aqueous and organic streams. Note: The density of water is a function of temperature, and is often less than 1000 kg/m³; therefore it is safer to specify a separation density below 950 kg/m³. |
| List of Liquid Individual Phases | Tick Boxes | Visible if SeparMethod = 'IndPhase to Organic'. The user must select one or more Individual liquid phases that will report to the Organic outlet. Normally, the user will select the 'o', or 'org' phase. All other liquid phases will report to the Aqueous outlet. (The user defines the Individual phase for each species in the Species Database. Normally organic species are defined to have an individual phase of 'o', or 'org'. Please see Individual Phase Label for information on how to change the Individual Phase of a species) |
| Entrainment | None | No entrainment. |
| Feed Loss | The Aqueous/Organic loss is defined as a percentage of the aqueous (or organics) in the unit after all the reactions have been completed. NOTE: This is feed to the separator section, not the mixer section. | |
| Product Fraction | The Aqueous/Organic loss is defined as mass concentration in the outlet stream, normally in ppm. | |
| AqueousLossReqd / AqsLossReqd | Input | Visible with the Feed Loss Entrainment method. The mass fraction of Aqueous liquid in the unit lost to the Organic product stream. Note that solids in the Aqueous phase will also report to the Organic stream when an entrainment value is specified. |
| OrganicLossReqd / OrgLossReqd | Input | Visible with the Feed Loss Entrainment method. The mass fraction of Organic liquid in the unit lost to the Aqueous product stream. |
| AqueousInOrgReqd / AqsInOrgReqd | Input | Visible with the Product Fraction Entrainment method. User specified the mass concentration of aqueous (normally in ppm) in the organic outlet stream. Note that solids in the Aqueous phase will also report to the Organic stream when an entrainment value is specified. |
| OrganicInAqsReqd / OrgInAqsReqd | Input | Visible with the Product Fraction Entrainment method. User specified the mass concentration of organics (normally in ppm) in the aqueous outlet stream. |
| Reactions | On/Off | The user may turn the reactions 'On' or 'Off'. If this is 'On' then the RB tab page will become visible. Reactions will be switched 'On' by SysCAD if the one of the isotherm method is chosen. |
| EnvironHX | On/Off | The user may turn the environment heat exchange 'On' or 'Off'. If this is 'On' then the EHX tab page will become visible. The heat exchange will occur after the reactions have taken place. |
| OperatingP - NOTE: this pressure is applied to the (combined) feed, before sub-models (if any). | ||
| Method | AutoDetect | If there are any liquids AND no vapours present in the feed, outlet streams will take the highest pressure of the feeds. Else (e.g. some vapours present) outlet streams will take the lowest pressure of the feeds. |
| LowestFeed | Outlet streams will take the lowest pressure of the feeds. | |
| HighestFeed | Outlet streams will take the highest pressure of the feeds. | |
| Atmospheric | Outlet streams will be at Atmospheric Pressure. The atmospheric pressure is calculated by SysCAD based on the user defined elevation (default elevation is at sea level = 101.325 kPa). The elevation can be changed on the Environment tab page of the Plant Model. | |
| RequiredP | Outlet streams will be at the user specified pressure. | |
| IgnoreLowMassFlow / IgnoreLowQm | Tick Box | This option is only visible if the AutoDetect, LowestFeed or HighestFeed methods are chosen. When calculating the outlet pressure and temperature of the tank, SysCAD will ignore the low flow feed streams should this option be selected. The low flow limit is set in the field below. |
| LowMassFlowFrac / LowQmFrac | Input | This field is only visible if the IgnoreLowQm option is selected. This is the amount any stream contributes to the total flow. For example, if the total feed to the tank is 10 kg/s, and this field is set to 1%. Then any feed streams with less than 0.1 kg/s will be ignored in the pressure calculations. |
| PressureReqd / P_Reqd | Input | This field is only visible if the RequiredP method is chosen. This is user specified pressure. |
| Result | Calc | The actual pressure used for the sum of the feeds which will also be the outlet pressure (unless further model options change the pressure). |
| ExtractionMethod / Method | None | The model does not use Isotherms to determine the extent of the extraction or stripping reaction. The user sets the extent/s of the reaction/s manually. |
| Isotherm2 | The model uses an Isotherm to determine the extent of a single extraction or stripping reaction. This option is retained for backward compatibility - use Multiple Isotherms.
| |
| Multiple Isotherms | The model uses multiple Isotherms to determine the extent of multiple extraction or stripping reaction.
| |
| Isotherms.Count | Input/Display | Only visible if ExtractionMethod is set to one of the Isotherm methods. If ExtractionMethod = Isotherm2, then this will be a result field set to 1. If ExtractionMethod = Multiple Isotherms, then this will be an input field. This field allows the user to set the number of isotherms they wish to define. |
| Mode (Only visible if ExtractionMethod is set to one of the Isotherm methods) | Extraction | select this mode for extraction of species from aqueous --> organic phase. |
| Stripping | select this mode for stripping the species from organic --> aqueous phase. | |
| PreMixEntrained | Tick Box | If enabled, aqueous material entrained in the organic feed will be assigned to the aqueous phase and vice-versa before feed measurements are performed. Additional result fields will be displayed to show the amounts of material transferred between phases. It is strongly recommended that this option be enabled if the Isotherm method is being used. |
Options | ||
| ShowEnergyBalance | Tick Box | Selecting this tickbox will add a energy balance section to the bottom of the results section of this tab. |
| ShowQAqFeed | Tick Box | QAqFeed and associated tab pages (e.g. Sp) will become visible if this is enabled. These tabs will show the properties of the combined aqueous feed stream to the Unit. Note this is before any premixing of entrained material from the organic feed. |
| ShowQOrgFeed | Tick Box | QOrgFeed and associated tab pages (e.g. Sp) will become visible if this is enabled. These tabs will show the properties of the combined organic feed stream to the Unit. Note this is before any premixing of entrained material from the aqueous feed. |
| ShowQFeed | Tick Box | QFeed and associated tab pages (e.g. Sp) will become visible if this is enabled. These tabs will show the properties of the combined feed stream to the Unit. These values are BEFORE any evaluation blocks such as reaction or EHX. |
| ShowQAqProd | Tickbox | Available from Build 139. When selected, the QAqProd and associated tab pages (e.g. Sp) will become visible, showing the properties of the aqueous outlet stream. See Material Flow Section. Tags in the QAqProd tab can be used for controllers (e.g.: PGM files) and reports even when this option is not selected. |
| ShowQOrgProd | Tickbox | Available from Build 139. When selected, the QOrgProd and associated tab pages (e.g. Sp) will become visible, showing the properties of the organic outlet stream. See Material Flow Section. Tags in the QOrgProd tab can be used for controllers (e.g.: PGM files) and reports even when this option is not selected. |
Operating Line | ||
| Organic/Aqueous / OARatio |
Calc | The calculated volumetric ratio of Organic to Aqueous liquid entering the unit. |
| Aqueous/Organic / AORatio |
Calc | The calculated volumetric ratio of Aqueous to Organic liquid entering the unit. |
PreMix EntrainedThis section is only visible if the PreMixEntrained tickbox is selected. | ||
| AdjustedAqQv | Calc | Liquid phase Volume flow of aqueous material in the feed after premixing. This will include any aqueous material which was entrained in the organic feed and exclude any organic material which was entrained in the aqueous feed. |
| AdjustedOrgQv | Calc | Liquid phase Volume flow of organic material in the feed after premixing. This will include any organic material which was entrained in the aqueous feed and exclude any aqueous material which was entrained in the organic feed. |
| TransferredAqQm | Calc | The mass of aqueous material in the organic feed which was transferred to the aqueous feed in the premixing step. |
| TransferredOrgQm | Calc | The mass of organic material in the aqueous feed which was transferred to the organic feed in the premixing step. |
Product Conditions | ||
| AqueousInOrg / AqsInOrg | Calc | The mass concentration aqueous in the organic outlet stream. |
| OrganicInAqs / OrgInAqs | Calc | The mass concentration organic in the aqueous outlet stream. |
| AqueousLosses / AqsLosses | Calc | The mass fraction of feed aqueous loss to the organic outlet stream. |
| OrganicLosses / OrgLosses | Calc | The mass fraction of feed organic loss to the aqueous outlet stream. |
| Isotherm.Iterations | Calc | The number of iterations required for isotherm calculations to converge. |
| OutletT.Iterations | Calc | The number of iterations required for outlet temperature calculations to converge. |
Energy BalanceThis section is only visible if the ShowEnergyBalance Option tickbox is selected. | ||
| Feed.Hz | (A) | The total energy for the incoming streams. (all aqueous and organic streams perfectly mixed) |
| Reaction.Ht@0 | (B) | The total heat of reaction of the RB block. |
| RB.HeatFlow | (C) | The delta heat flow from RB - Heat exchange. (This is added via the Reaction block, if used a RHX tab will be visible) |
| MixAfterRB.Hz | (=A-B+C) | The total energy for the contents after Reactions, before EHX. |
| EHX.HeatFlow | (D) | The delta heat flow from Environmental Heat Exchanger (EHX). (This is added via the EnvironHX option, if used a EHX tab will be visible.) |
| Prod.Hz | (=A-B+C+D) | The total energy for the mixture after reactions and EHX. |
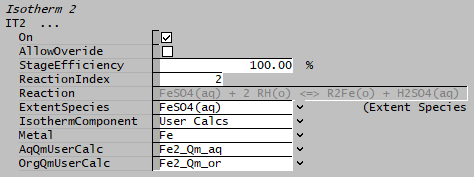
ITX Page
One page will be displayed for each isotherm, IT1, IT2, IT3, etc. The number of isotherms (Isotherms.Count) is set by the user on the Solvent Extraction page. On this page, the user defines the data for the isotherm including defining which reaction the isotherm controls. See also Hints and Comments.
| Tag (Long/Short) | Input / Calc | Description/Calculated Variables / Options |
| On | Tickbox | If this is enabled then the isotherm will be used to control the extent of the user specified reaction. If this is disabled, then the isotherm will be ignored and the reaction extent can be set directly by the user. |
| AllowOveride | Tickbox | This allows the user to override the reaction extent calculated by the isotherm and manually set the reaction extent on the RB tab page. An Access window notification is given in to remind the user that override is in use. |
| StageEfficiency / StageEff | Input | The efficiency of the solvent extraction stage. This factor is to take into account that the two phases may not be in contact long enough to achieve perfect equilibrium. The stage efficiency reduces the calculated reaction extent by the user-specified stage efficiency. |
| ReactionIndex | Input | The number of the reaction to be controlled by the isotherm. |
| Reaction | Display | This displays the actual reaction in the reaction file (based on the ReactionIndex selection). This is a standard tagged object and hence it can be copied and pasted and used in reports, etc. |
| ExtentSpecies / ExtentSp | Input | The reaction species that contains the primary metal, e.g. for Extraction it may be CuSO4, and for Stripping R2Cu. |
| IsothermComponent | Element | If the isotherm data is based on a selected element, and its concentration represents the total elemental concentration in the that phase, then set this to element. |
| User Calcs | In some cases, the total elemental concentration may not be used directly, for example, Fe can be in the form of Fe2+ and Fe3+. If user only wish to get the Fe2+ concentration and not the total Fe concentration, then user specified calculations should be used. Please see example 2 for more information on how to set up the user calculations. | |
| PrimaryMetal | List | Only visible when IsothermComponent = Element. User can select an element from the available list. This should be the element for which the isotherm data is based on. For example, if the isotherm data is for Cu, then we would select Cu as the element here.
|
| Metal | List | Only visible when IsothermComponent = User Calcs. User can select an element from the available list. This should be the element for which the isotherm data is based on. For example, if the isotherm data is for Cu, then we would select Cu as the element here. |
| AqQmUserCalc | List | Only visible with the "User Calcs" option. Using the example of Fe2+, if the concentration should be based on Fe2+ from species FeSO4(aq) only, then user must define a user property calculation for Fe2+ mass flow in the aqueous phase. This user property calculation name should be set here.
|
| OrgQmUserCalc | List | Only visible with the "User Calcs" option. Using the example of Fe2+, if the concentration should be based on Fe2+ from species R2Fe(o) only, then user must define a user property calculation for Fe2+ mass flow in the organic phase. This user property calculation name should be set here.
|
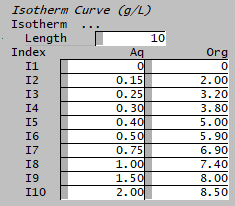
Isotherm Curve (g/L) | ||
| Isotherm... | ||
| (The user enters the data points in the two columns on this page. For example, for extraction, Aq represents the mass fraction of solute in raffinate, and Org represents the mass fraction of solute in extract. The model interpolates linearly between the points and extrapolates beyond the first and last points.) | ||
| Length | Input | The number of data points. Once a number has been typed in, the X and Y columns will be visible with the required number of lines. If the data is loaded from a predefined file, the length will be automatically set to match the file length. |
| Data Points | Index | The data point index value |
| X axis value | The Aqueous or Organic values for the Isotherm. For extraction, the x-axis is for the aqueous phase; for stripping, the x-axis is for organic phase. | |
| Y axis value | The Aqueous or Organic values for the Isotherm. For extraction, the y-axis is for the organic phase; for stripping, the y-axis is for aqueous phase. | |
| (The isotherm data can be saved to or loaded from a file.) | ||
| FileName | Input | User specified filename, (1) to store current screen values or (2) load pre-defined values. The file should be in a CSV (comma delimited) format. |
| Folder | Display | When saving the data to a file, the default folder will be the current project folder unless specified otherwise by the user. |
| Edit | Button | This will open the isotherm data CSV file (as entered on in the FileName field) for editing. If no filename has been specified, pressing this button will open a new XXXX.csv file for editing. XXXX is the name of the current unit operation. |
| Reload | Button | Only active if FileName is not empty. This will load the data points from the CSV file, replacing the current values. |
| Save | Button | Only active if FileName is not empty. This will save the current values to the CSV file. |
| Browse | Button | Use the "Browse" button to locate the CSV file that contains the isotherm data. |
Results | ||
| MinOrgConc OR MinAqsConc | Calc | The Y-intercept of the McCabe-Thiele operating line, MinOrgConc in the case of extraction, and MinAqsConc in the case of stripping. NOTE this is defined by the feed streams entering the unit operation. This field will be set to zero if the Isotherm is switched off. |
| ReactExtentIso | Display | This is the calculated reaction extent required based on the Isotherm calculations. If override has been enabled the user can choose a different value (shown in the next field) and this will be displayed for reference only. This field will be set to zero if the Isotherm is switched off. |
| ReactExtent | Display | This is the reaction extent required as appears on the RB tab page. If override has been enabled, this will show the value entered by the user. Displayed here for easy access. |
| ReactExtentAchieved | Display | This is the actual reaction extent achieved as appears on the RB tab page. Displayed here for easy access. |
| MaxPriConcOrg | Calc | Visible if Extraction Mode is chosen. Displays the maximum primary element or user compound in organic product. This will serve as a warning for incorrectly supplied data if the results differ to those expected. |
| MaxPriConcAq | Calc | Visible if Stripping Mode is chosen. Displays the maximum primary element or user compound in aqueous product. This will serve as a warning for incorrectly supplied data if the results differ to those expected. |
| Feed Conditions | ||
| AqueousConcIn / AqsConcIn | Calc | The concentration of the "total primary metal element" or "user compound" in the incoming Aqueous stream. |
| OrganicConcIn / OrgConcIn | Calc | The concentration of the "total primary metal element" or "user compound" in the incoming Organic stream. |
| Product Conditions | ||
| AqueousConcOut / AqsConcOut | Calc | The concentration of the "total primary metal element" or "user compound" in the outgoing Aqueous stream. |
| OrganicConcOut / OrgConcOut | Calc | The concentration of the "total primary metal element" or "user compound" in the outgoing Organic stream. |
Aq(g/L),Org(g/L) 0.00,0.00 0.15,2.00 0.25,3.20 0.30,3.80 0.40,5.00 0.50,5.90 0.75,6.90 1.00,7.40 1.50,8.00 2.00,8.50 |
Adding this Model to a Project
Add to Configuration File
Sort either by DLL or Group:
| DLL: | Separation.dll |
→ | Units/Links | → | Separation: Solvent Extraction (Mixer/Settler) | |
| or | Group: | Mass Separation |
→ | Units/Links | → | Separation: Solvent Extraction (Mixer/Settler) |
See Model Selection for more information on adding models to the configuration file.
Insert into Project Flowsheet
| Insert Unit | → | Separation | → | Solvent Extraction (Mixer/Settler) |
See Insert Unit for general information on inserting units.
Hints and Comments
- Check that the Separation Density specified in the model is a value between the aqueous and organic densities.
- If the isotherm is required to be used outside the range of the data points entered, then SysCAD will linearly extrapolate from the nearest set of 2 points.
- Isotherm data points (both Aq and Org) are expected to increase in value. Data points will be sorted automatically from lowest to highest value as the data points are entered or loaded from the file.
- Isotherm data plot X and Y axes are in concentrations (g/L).
- For extraction, the x axis is the concentration of the primary metal in the aqueous phase and the y axis is the concentration of the primary metal in the organic phase.
- For stripping, the x axis is the concentration of the primary metal in the organic phase and the y axis is the concentration of the primary metal in the aqueous phase.
- If the primary metal element is present in multiple species, and only selected species should be counted, then user should specify which species are included by defining "user property calculations". Please see example 2 on how to set up user calculations. It is important that the same species definition is defined for both the aqueous and organic phase. (See Further Discussion for more information.)
Further Discussion
Suppose we have an SX unit with 3 reactions (as per the Nickel Copper Project):
1. CuSO4(aq) + 2 RH(o) <=> R2Cu(o) + H2SO4(aq)
2. Fe2[SO4]3(aq) + 6 RH(o) <=> 2 R3Fe(o) + 3 H2SO4(aq)
3. FeSO4(aq) + 2 RH(o) <=> R2Fe(o) + H2SO4(aq)Let's first look at reaction 1, where Cu is only present in 1 reaction.
- If we want to use isotherm for Cu (to set the extent for Reaction 1), we can declare the isotherm as follows:
- Select the "IsothermComponent" as "Element",
- Specify the "Primary Metal" as "Cu" and specify an Isotherm with units of g/L Cu along both axes.
- The "ReactionIndex" is specified as 1, for the first reaction and the Model will find an equilibrium Operating Point for the concentration of elemental Cu in each of the Product streams.
- These results are used to determine the Reaction Extent for R1 as the fraction CusSO4 reacting.
- The Product concentrations of elemental Cu as calculated from the CuSO4(aq) and R2Cu(o) concentrations in the Product will be consistent with the Operating Point calculation.
Next, we will look at Fe, note that Fe is present in both R2 and R3. If we use Fe as the Primary Metal as we did for Cu, then we may encounter some "interference" if both of the Fe reactions are on. For example:
- Declare the "IsothermComponent" as "Element" and specify the "Primary Metal" as "Fe", and
- Define an Isotherm with units of g/L Fe along both axes,
- The Model will find an equilibrium Operating Point for the concentration of elemental Fe in each of the Product streams.
- If R3 is turned off and there is no FeSO4 present then the Product concentrations of elemental Fe as calculated from the Fe2[SO4]3(aq) and R3Fe(o) concentrations in the Product will be consistent with the Operating Point calculation, as described above for Cu.
- However, if R3 does result in conversion of some FeSO4(aq) to R2Fe(o), the elemental Fe concentrations in the Product streams will not be consistent with the calculated Operating Point since:
- Feed elemental Fe(aq) and Fe(o) concentrations include contributions from both Fe species; and
- Product elemental Fe(aq) and Fe(o) concentrations include contributions from both Fe species.
To solve the above issue, we can define separate isotherms for Fe2+ and Fe3+, so that both reactions can be set using isotherms without interfering the other.
- For example, define a separate Isotherm in terms of Fe3+ for use in reaction 2. The user calculation defined should be:
- Fe3+_aq = Mass flow of Fe in Fe2[SO4]3(aq);
- Fe3+_or = Mass flow of Fe in R3Fe(o)
- Declare the "IsothermComponent" as "User Calcs"
- Define the Isotherm in terms of Fe3+_aq on one axis and Fe3+_or on the other axis (which is to say, in terms of Fe3+ on both axes)
- Then the model will find equilibrium product concentrations of Fe3+ in each Product stream and the Product concentrations of each of the User Components as calculated from the Product streams Fe2[SO4]3(aq) and R3Fe(o) concentrations will be consistent with the Operating Point Calculation.
- Likewise, define a separate Isotherm in terms of Fe2+ for use in reaction 3. The user calculation defined should be:
- Fe2+_aq = Mass flow of Fe in FeSO4(aq);
- Fe2+_or = Mass flow of Fe in R2Fe(o)
NOTE: the above examples are using stage efficiency of 100%.