Python Example - CFEM
Navigation: User Guide ➔ COM Automation ➔ Python Automation ➔ Example - CFEM
Constrained Free Energy Minimization
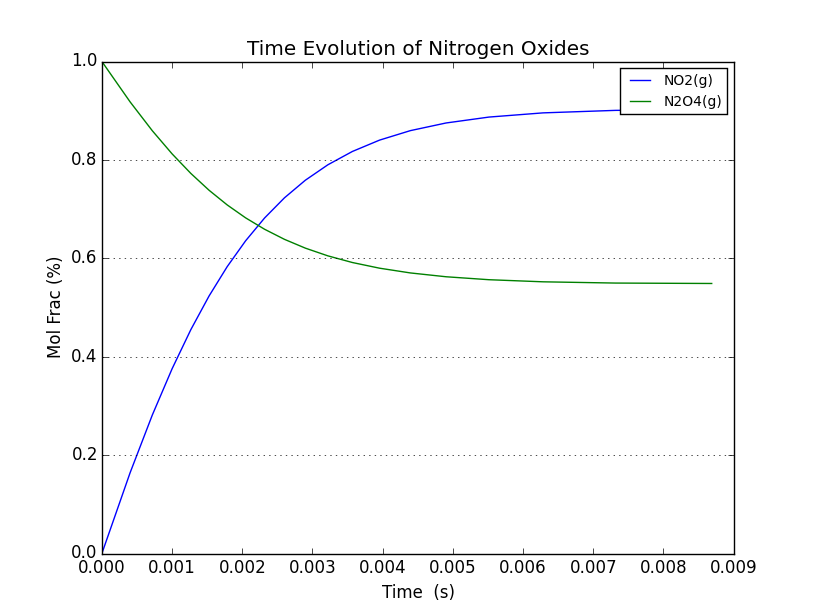
This example demonstrates time evolution of N2O4 decomposition using FEM lockup to constrain the reaction N2O4=2NO2, and then calculate the evolution of the reaction. The python numerical libraries can manipulate large data arrays and are invaluable for complex calculations.
The rate equation is
- [math]\displaystyle{ \cfrac{d[N_2O_4]}{dt} = k[N_2O_4]\left(1-\cfrac QK\right)\qquad }[/math](1)
- where
- Q is the reaction quotient
- K is the equilibrium value of the reaction quotient.
- k is the rate constant: [math]\displaystyle{ k=A\exp{\left(\cfrac{-E_a}{RT}\right)} }[/math]
- See Introduction to constrained Gibbs energy methods in process and materials research, Pertti Koukkari.
Rather than integrate this directly, we rewrite as:
- [math]\displaystyle{ {\Delta t} = \cfrac{\Delta[N_2O_4]}{k[N_2O_4]\left(1-\cfrac QK\right)}\qquad }[/math](2)
which determines the time [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta t }[/math] for a change in concentration.
import math
import time
import win32com.client as wc ## COM interface
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ## Plotting graphics
import numpy as np ## Numerical python
def RunScenarios(XVals, setTag, getTagLis, verbose=True, sleepTime = 5):
'''"""Run a number of scenarios with setTag set to the values in vals, and accumulate the'''
'''values of tags in getTagLis"""'''
Y = []
for x in XVals:
if verbose: print (x)
Tags.SetTagValue(setTag, x) ## Change tag value
ProBal.Start()
while True: ## Wait until solved
if verbose: print ("Solving...")
time.sleep(sleepTime)
if ProBal.IsStopped:
break
Y.append([Tags.TagValue(s) for s in getTagLis])
return Y
ver = 93 ## Recent versions of SysCAD use a different COM ID
ProgID = "SysCADSimulator.Application" if ver<93 else "SysCADSimulator93.Application"
ScdDir = r'C:\93Files'
ScdPrj = r'\Nitrogen\CFEM Demo.spf\Project.spj'
SysCAD = wc.DispatchEx(ProgID) ## Fire up SysCAD
Prj = SysCAD.OpenProject(ScdDir+ScdPrj) ## Open project
Tags = Prj.Tags
Solver = Prj.Solver
ProBal = Solver.ProBal
Prod = [
"NO2(g)" , # 0
"N2O4(g)" , # 1
]
prodTagLis = [("P_002.Qo.QMl.%s (kmol/h)" % c) for c in Prod]
l1 = 100*(1.-np.linspace(0, 1, 20)**2) ## generate a linear space but increase resolution by squaring it
lkup = l1[::-1] ## reverse it
def genData():
Tags.SetTagValue("FEMR_001.T_Reqd (C)", 40)
Tags.SetTagValue("FEMR_001.OperatingP.P_Reqd (atm)", 1.0)
res = [(0.0, 1.0)]
res.extend(RunScenarios(100-lkup[1:], "FEMR_001.FEMD.[N2O4(g)].Lockup (%)", prodTagLis, sleepTime= 0.2))
return np.array(res)
rp = genData()
Ea = 40.e3 ##81.e3
R = 8.3144
T_K = 273.15+40
A = 1.0e9
k = A*math.exp(-Ea/(R*T_K))
rr = rp/rp[-1] ## Concentration/EquilibriumConcentration
Affinity = 1.-rr[:, 0]**2/rr[:, 1] ## Affinity
DeltaN2O4 = -np.diff(rp[:, 1]) ## Change in [N2O4]
N2O4Term = k*(rp[:-1, 1]+rp[1:, 1])/2. ## Average value of [N2O4] in each time step
DeltaT = DeltaN2O4/N2O4Term/Affinity[:-1] ## Delta Time for each reaction extent change
T = np.insert(np.cumsum(DeltaT), 0, 0) ## Actual (cumulative) time
def doPlot():
plt.ion()
for Y, lbl in zip(rp.transpose(), ["NO2(g)", "N2O4(g)"] ):
plt.plot(T, Y, label= lbl)
plt.legend(fontsize='small')
plt.ylabel("Mol Frac (%)")
plt.xlabel("Time (s)")
plt.grid(axis='y')
plt.title("Time Evolution of Nitrogen Oxides")
plt.show()
SysCAD.CloseProject(False)
time.sleep(1)
del(Solver)
del(Tags)
del(Prj)
del(SysCAD)
doPlot()
We run a series of FEM equilibrium calculations with the species N2O4 from completely locked up (100%), to unconstrained (0%, hence equilibrium). From the data, we then calculate the time required for each step change via a rate equation, and generate a plot of the time evolution.