ChemApp Database Utility
|
NOTE: This feature is currently in BETA with limited release. Please contact us ([email protected]) if you are interested in using this model. This page is currently under development and details may change. Use with caution - we do not guarantee compatibility between different BETA versions. |
Navigation: Models ➔ TCE Models ➔ ChemApp ➔ ChemApp Database Utility
| ChemApp Overview | ChemApp Database Utility | ChemApp Model Configuration | ChemApp Direct Calc | ChemApp Side Calc | ChemApp Reactor | ChemApp Feeder | ChemApp Tank (Dynamic) |
|---|
Latest SysCAD Version: 25 October 2024 - SysCAD 9.3 Build 139.36522
Applicability
This utility is for adding a list of species into a new SysCAD.93.db3 file for use with ChemApp TCE.
- It will use data from existing databases (in SysCAD database format), examples of such are Default.93.db3, SysCAD.93.db3 from user projects (these can be renamed for better identification).
- It will NOT extract data from ChemApp FactSage databases.
- It will add species to the new database based on the DAT or CST files selected.
- If a species is not found in the existing database, it will add the species with minimum data (Long Name, Short Name, compound, definition, phase, occurrence), but will leave all the other properties blank. User will need to check and fill in data from other sources after the database is created.
General Information
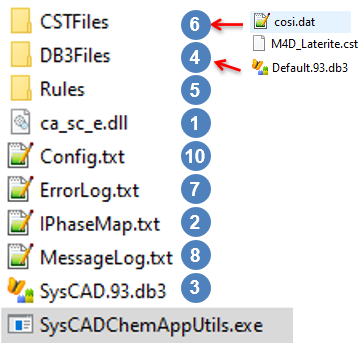
Utility file name: SysCADChemAppUtils.exe
- This utility can be used to create a species database using data from ChemApp DAT or CST (encrypted model file) file.
- The utility can be placed in any folder, but the folder must meet the following requirements:
- The following ChemApp DLL file should be placed inside the folder (copy from the ChemApp install folder):
- User with Full ChemApp License: The "ca_sc_e.dll" must be present in the utility folder
- User with ChemApp Light: The "ca_vc_l.dll" must be present in the utility folder.
- The "ca_sc_e.dll" has precedence over "ca_vc_l.dll", ChemApp Light users should rename or delete the "ca_sc_e.dll" from the utility folder.
- There must be an “IPhaseMap.txt” file in the same folder, a template will be created if one does not exist. See Creating the IPhaseMap.txt
- User must edit this file to contain the correct mapping information before the database can be created correctly.
- There must be an existing SysCAD.93.db3 file inside the folder to serve as a template (for species table layout).
- CAUTION: this file will be stripped down to contain only water and steam, then new data will be added based on the ChemApp model species list.
- Please use a “copy” of the actual SysCAD.93.db3 file to avoid destroying user data.
- There must be a subfolder, “DB3Files”, containing the following files:
- May contain the Default.93.DB3 file (copy from SysCADxxx\BaseFiles folder).
- May contain user’s own database files, formatted in SysCAD DB file format.
- Any database files stored in the DB3Files subfolder will be used to populate the SysCAD.93.DB3 file.
- when more than one database is present, there may be multiple entries for the same species, if a species has multiple sets of data, user must choose which set of data to add to the SysCAD.93.DB3 file.
- as an alternative to the above, user can specify a preferred database. In this case, the preferred database will be used whenever possible, with alternate databases used elsewhere and placeholder species created where no data is available. Selecting a preferred database will avoid choosing data for each case where multiple options are available.
- The databases in this folder will be used to build a list of options presented to the user by the utility.
- There must be a subfolder, “Rules”, containing the following files:
- Must contain a Liquids.txt file. This specifies a number of substrings which are used to identify a ChemApp phase as a liquid. For example, the supplied Liquids.txt file contains: "AQU", "LIQ", etc., each on its own line. The user can add additional substrings which will be used by the utility to identify a ChemApp phase as a liquid.
- Must contain a Gases.txt file. This specifies a number of substrings which are used to identify a ChemApp phase as a gas. For example, the supplied Gas.txt file contains: "GAS". The user can add additional substrings which will be used by the utility to identify a ChemApp phase as a gas.
- There is no Solids.txt file. Any phase that is not identified as a liquid or a gas, based upon the substrings defined in Liquids.txt and Gases.txt, is defined as a solid.
- There must be a subfolder, “CSTFiles”:
- Users with Full ChemApp: must place copies of each CST file that they wish to include in the generation of the SysCAD database file.
- Users with ChemApp Light: must place copies of each DAT file that they wish to include in the generation of the SysCAD database file.
- There is an option to select one or all of the contained CST (DAT) files.
- An ErrorLog.txt file is generated in all cases. It contains any errors encountered while running the utility and should be reviewed after generation of the SysCAD database.
- A MessageLog.txt file is generated in all cases. It contains general messages generated while running the utility and should be reviewed after generation of the SysCAD database.
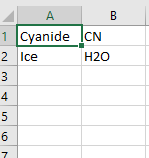
- Optional: User can place a Replacements.txt file in the same folder as the executable. This is a tab-delimited file that contains replacement strings. If not found, it is simply not used.
- If the above file were used, any ChemApp species containing the string Ice would be replaced with H2O in the creation of SysCAD species.
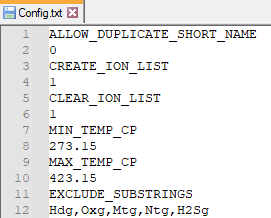
- Optional: User can place a Config.txt file in the same folder as the executable. This is a formatted file that contains configuration settings. If not found, it is simply not used.
- INCLUDE_ELEMENTS: specify in the line below this keyword the elements you want to include, comma separated list.
- EXCLUDE_ELEMENTS: specify in the line below this keyword the elements you want to exclude, comma separated list.
- INCLUDE_OCCURRENCES: specify in the line below this keyword the occurrences you want to include, comma separated list. Can be s, l, or g.
- INCLUDE_PHASES: specify in the line below this keyword the phases you want to include, comma separated list. These are substrings, thus, in the example above, any phase which contains slag (case insensitive) would be included.
- EXCLUDE_SUBSTRINGS: specify in the line below this keyword any substrings within species that you want to exclude, comma separated list. For example, entering C2, C3, C4 (case sensitive) would exclude ethyl, propyl, and butyl species.
- ALLOW_DUPLICATE_SHORT_NAME: specify in the line below this keyword either 0 (false) or 1 (true). If you allow duplicate short names, the short names will be appended with _1, then _2, etc. For example, if you have multiple types of silica, you would get SiO2, SiO2_1, SiO2_2, etc.
- CREATE_DEFAULT_SPECIES_IF_NO_MATCHES_FOUND: specify in the line below this keyword either 0 (false) or 1 (true). If you allow default species to be created, you will get default species (with no thermodynamic or properties data) as placeholders when a matching species is not found. If false, only matched species will be added to the database (with thermodynamic and properties data taken from the db3 file). Default value is true.
- MIN_TEMP_CP: specify in the line below this keyword the desired lower bound temperature of the heat capacity correlation for selection, in K. The utility will use this if, in the selection of the database, you choose -1. It will then find the matching database entry with the greatest Cp range within the desired range.
- MAX_TEMP_CP: specify in the line below this keyword the desired upper bound temperature of the heat capacity correlation for selection, in K. The utility will use this if, in the selection of the database, you choose -1. It will then find the matching database entry with the greatest Cp range within the desired range.
- Example for Cp Range: Consider where MIN_TEMP_CP is 273 K and MAX_TEMP_CP is 423 K. There are two possible species matching, one with a range of Range(K,273,450), and another with a Range (K,500,1500). Even though the second has a greater Cp Range than the first, its range is fully outside of the desired range, and thus, it will be rejected in favour of the first, which has a smaller range, but its range fully encompasses the desired range defined by MIN_TEMP_CP and MAX_TEMP_CP. Selections by this method are logged in the ErrorLog.txt file.
- USE_HARDWIRED_DATA: specify in the line below a value of 1 (true) or 0 (false). If true, it will use "hardwired" data from SysCAD and some additional data from NBS Tables when no data is available for a specific property and species.
- If no Config.txt file exists, all species are loaded unfiltered.
- FORCE_UPPER_CASE_PHASE_NAMES: specify in the line below this keyword 1 (true) or 0 (false). If true, all phases read from the database file will be forced to all upper case. Default is false. Only applicable when the phase names are derived from actual names (applicable to ChemApp).
- The following ChemApp DLL file should be placed inside the folder (copy from the ChemApp install folder):
How to use the Utility
The utility has two functions:
- assisting with the creation of IPhaseMap.txt. This file must be completed before user can move on to the next step.
- creating the SysCAD.93.db3 file.
The theory behind mapping between SysCAD and ChemApp species is described in ChemApp Model Configuration Model Theory. Please ensure you have a clear understanding of this before proceeding to use the utility to generate a SysCAD database and configuration files.
Defining IPhaseMap.txt
The IPhaseMap.txt file is used to map between phase names in the ChemApp model file (CST or DAT file) and individual phases within SysCAD. A phase here is a grouping of species which exist together in a homogeneous mixture. This differs from an occurrence, which can be a group of phases. For example, liquid metals may form a phase, while slags may form another phase, but together, these are part of a liquid occurrence. In addition, there may also be pure phases within ChemApp, which are phases which have only one species within them.
The three mandatory columns within the IPhaseMap.txt file are described in the table below.
In SysCAD, pure phases may be treated as an individual phase or as part of an occurrence. In IPhaseMap.txt file, this would be represented as:
- Part of individual phase (there must be a SysCAD individual phase Q, and will map to SysCAD species SiO2(Q)):
- Part of occurrence (this will map to SysCAD species SiO2(s)):
NOTE: If user is to create a new SysCAD database file with no ChemApp phase information, then it is best to start with NO "IPhaseMap.txt" file, this will allow the utility to create a template for you. To do so, delete the IPhaseMap.txt file before starting the utility. If in doubt of the validity of the IPhaseMap.txt file, the user is encouraged to regenerate it.
Creating IPhaseMap.txt
The following instructions are for user with NO valid IPhaseMap.txt file. User must run the utility once to generate a valid IphaseMap.txt, then proceed with Creating the database with a valid IPhaseMap.txt to generate the database.
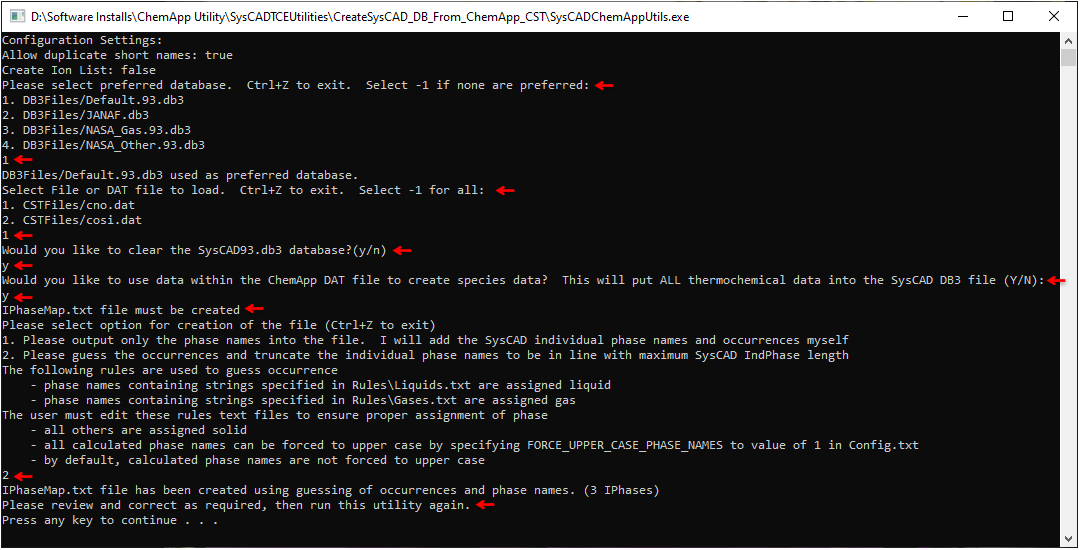
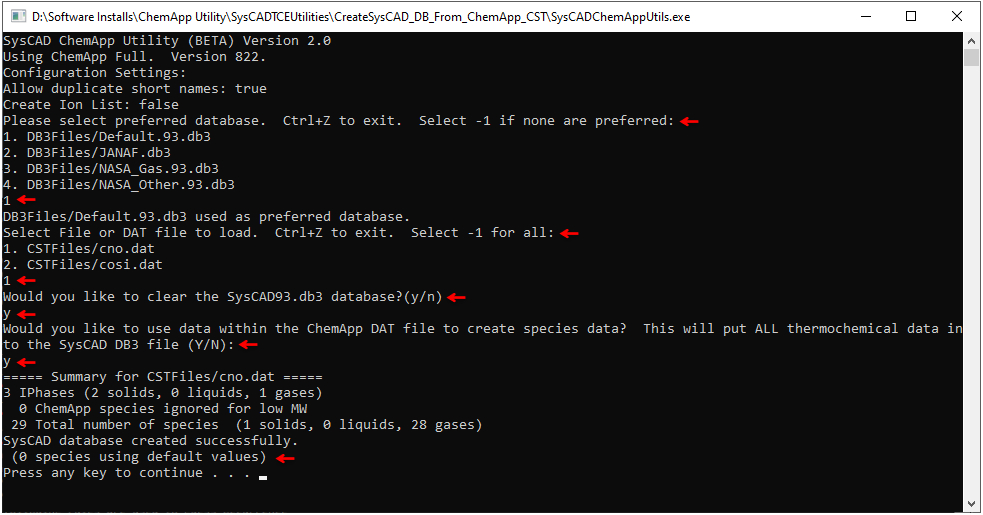
- Run SysCADChemAppUtils.exe
- The utility will ask for selection of a preferred database. Select the corresponding preferred database, or -1 if none is preferred. If -1 is selected, the user will manually select the data for each species where more than one option exists (see later step).
- Select the CST (or DAT) file for which you wish to create a database and IPhaseMap.txt file. Select -1 to create files which incorporate all of the CST (or DAT) files in the CSTFile folder.
- The Utility will create the IPhaseMap.txt file using one of TWO options:
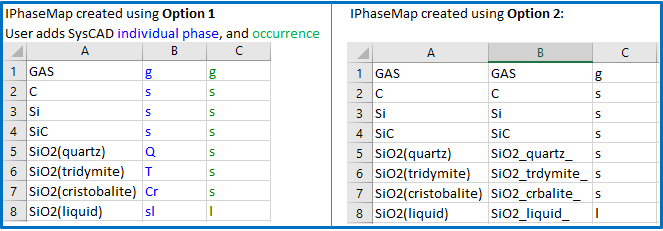
- OPTION 1: The IPhasemap.txt file will be created with ChemApp phases only. User MUST edit the IPhasemap.txt file to manually assign corresponding SysCAD individual phase mapping and occurrence. A file "Instructions.txt" will be created with instructions on how to edit the “IPhaseMap” file. The IPhaseMap.txt edited (manually) for the cosi.dat is shown below (left image) as an example.
- OPTION 2: The IPhasemap.txt file will be created with SysCAD individual phase names according to some predefined "RULES". The user is STRONGLY recommended to review and possibly correct the resulting SysCAD individual phase mapping before continuing with database creation. Phase names are created based upon formulas and truncated for length. Occurrences (i.e. solid, liquid, or gas) is guessed for each phase by trying to find the substrings listed for liquids or gases. The IPhaseMap.txt create for the cosi.dat is shown below (right image) as an example.
- Optional columns for pure phase options:
- For pure phases, you can manually add two additional columns to control how the utility manages pure phases in the creation of the database files and configuration. The additional columns and their effect on the utility behaviour are described in the table below:
- If these columns are not included, the SysCAD phase name is appended to the long name by default. Consider the species SiO2(Quartz) once again. In this case, the long name of the SysCAD species would be:
- Silica.[Q] where Q is the SysCAD phase corresponding to the ChemApp phase SiO2(Quartz).
- This is the default behaviour. If the columns are added and a 0 is specified in column 4, it will now create an individual phase "Q" and create the species SiO2(Q).
Once the iPhaseMap.txt has been created, please check the file before proceeding with the next step.
Creating the database with a valid IPhaseMap.txt
The following instructions are for users with a valid and checked IPhaseMap.txt.
- Run SysCADChemAppUtils.exe
- The utility will ask for selection of a preferred database. Select the corresponding preferred database, or -1 if none is preferred. If -1 is selected, the user will manually select the data for each species where more than one option exists (see later step).
- Select the CST (or DAT) file for which you wish to create a database and IPhaseMap.txt file. Select -1 to create files which incorporate all of the CST (or DAT) files in the CSTFiles folder.
- Where a suitable species does not exist in the available SysCAD database source files, a placeholder species will be created with NO thermodynamic data.
- Note that if you are loading a DAT file (i.e. where the data is not protected), the Gibb's energy function listed in the DAT file will be used to construct the corresponding Gibbs_Cp or GibbsChemAppCp function in the SysCAD database for this species. Only Gibbs_Cp and GibbsChemAppCp (equation types 1 and 4, respectively) are currently supported.
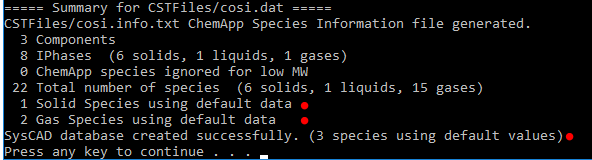
- Upon completion, the utility will show a summary, confirming the database was created successfully. Press any key to close the utility.
- NOTES:
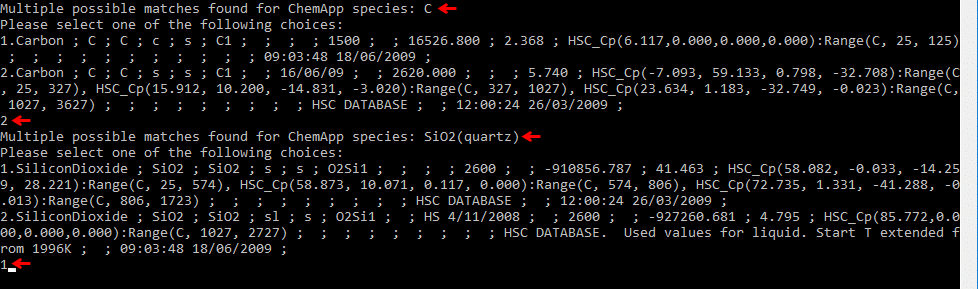
- While running the utility, if you have NOT selected a preferred database and multiple data is found for a species, you will be prompted to select one of the options. In the example below, the utility has found 2 sets of data for “C” in the available databases, we have selected data set 2 by typing in the "2". For SiO2 quartz, we have selected data set 1.
- If the species data does not exist in the reference SysCAD databases, then a place holder species with no thermodynamic or physical properties data will be used. When this happens, any project using this database will log appropriate warnings on load, look out for these species when Checking the Created SysCAD.93.db3
- User can use <Ctrl+Z> to quit the utility at any time.
Checking the Created SysCAD.93.db3
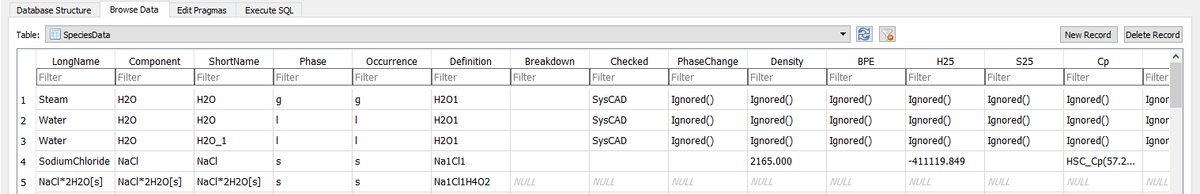
- Check the SysCAD.93.db3 file before copying it to your actual project's cfgfile folder. You can use any SQLite DB reader, such as DB Browser for SQLite. View the SpeciesData table to see the data. Species for which no data was found in the reference databases will appear as having each of the definition columns filled, but all of the property columns blank. In the example below, NaCl*2H2O is using placeholder data.
- An error will occur if a SysCAD individual phase or occurrence is missing, the utility will stop once this occurs. User has to fix the IPhasemap.txt file, then run the utility again.
Copy the files to the CfgFiles folder
Generally speaking, user only need to use this Utility to generate the SysCAD.93.db3 file at the start of a new ChemApp project group. Once the database has been created, the SysCAD.93.db3 and IPhaseMap.txt files, as well as the associated CST files used to generate them, should be copied to the ChemApp SysCAD project group\CfgFiles subfolder. For SysCAD with ChemApp flowsheets using multiple CST files, it is required to create the database using all of the CST files at the same time when using this utility.
Updating the SysCAD Configuration
- Edit the SysCAD configuration
- Open SysCAD without a project open. Go to Edit->Project Configuration
- Edit the new configuration. Press "Next" on the Step 1 of 2 dialog.
- In the Step 2 of 2 dialog, go to the species tab, then add the required species to the project.
- Go to the TCEs tab
- Update the configuration for ChemApp. See TCE Configuration Help Page for more information.
NOTES: To select ALL species for the project:
- Select the first species in the middle column, hold shift, and select the last species in that column. This will select ALL species in the database.
- Add all species to the project by pressing the "Add Species>>" button.
Creating a Test Project
You should now have a working SysCAD configuration file. The next step is to create a project and review the species properties.
- Create a new SysCAD project and select the newly created configuration. See Introductory Tutorial - Creating a SysCAD Project for more details.
- Once the project is open, review the species properties
- Go to Species->View Properties
- This brings up a window showing all data used for all species. More information on this window is here: Species Properties ($SDB). It is recommended to carefully review this to ensure it is correct.
Troubleshooting
| Error | Description | Possible cause / suggested solution. |
|---|---|---|
| Utility Startup Errors | Missing SysCAD Template species database (SysCAD.93.db3) | The SysCAD.93.db3 file is missing from the Utility folder. This file is required as a starting point. User may copy any valid SysCAD.93.db3 file from the SysCADxxx folder here. |
| No SysCAD reference species database found in folder DB3Files | The "DB3Files" folder is missing or empty. Please check the folder name and or make sure it contains at least one SysCAD database, such as the Default.93.db3 | |
| No ChemApp CST files found in folder CSTFiles | The "CSTFiles" folder is missing or empty. Please check the folder name and or make sure it contains at least one ChemApp model files with extension .CST or .DAT. | |
| IPhaseMap.txt not created properly | IPhaseMap.txt file must be created. | The "Rules" folder missing or not complete. Please check the folder name and make sure it contains rules for Gas and Liquid. |
| Database not created successfully | Some ChemApp phases were not assigned corresponding SysCAD individual phases | Caused by missing data in the IPhaseMap.txt, likely a result of an unchecked IPhaseMap.txt file prior to running the utility.
|
| Error Number: 103 | The thermodynamic data-file could not be completely entered due to a read error | This error is generated if the ChemApp Model file contain "abnormal data", please contact SysCAD support to investigate. |
| Error Number: 160 | The thermochemical system is too big (NA=XX, Max:30) for this version of ChemApp | This error is generated if ChemApp light user attempts to load in a ChemApp model file containing more than 30 ChemApp species. ChemApp full version is required if user wants to use the specified ChemApp model file. |
| Error Number: 163 | No Valid dongle found | This error is generated if no valid ChemApp license is found. If user is using ChemApp Light, please rename the "ca_sc_e.dll" file to remove it from the utility's search path. |
Recommended Procedure
The following steps are recommended in the creation of a new configuration to match a TCE database. These steps are applicable for all of the TCE packages (PHREEQC, AQSol, OLI, and ChemApp). Note that ChemApp requires an additional file, IPhaseMap.txt.
- Create a SysCAD database
- Extract the utility files to a folder of your choice
- Copy the TCE database file into the DatabaseFiles (CSTFiles for ChemApp) folder of that utility folder structure, e.g. for PHREEQC, this will be a DAT file, for OLI, this will be a DBS file, etc. This step is not applicable to AQSol.
- Update the settings in the Config.txt file.
- Run the utility to generate a database file.
- Create a SysCAD configuration
- Open SysCAD without a project open. Go to Edit->Project Configuration
- In the resulting dialog, create a new configuration. Give it a name of your choice. Press OK when done.
- Edit the newly created configuration. In the Step 1 of 2 dialog, enable the TCE interface that you are using, i.e. enable the ScdOLI2, ScdPHREEQC, ScdAQSol, or ScdChemApp dll. Press Next. Then press OK.
- Right click on the project configuration that you just created, select "Open Containing Folder" to open that folder in windows explorer.
- Copy the TCE database file into the new configuration, i.e. into the CfgFiles folder. This can be done using windows explorer. This could be a dat, dbs, or CST file. Note that there is no file associated with AQSol.
- Copy over the SysCAD93.db3 file generated (the SysCAD database), the IonList.txt file, and the IPhaseMap.txt file (if using ChemApp).
- Edit the SysCAD configuration
- Open SysCAD without a project open. Go to Edit->Project Configuration
- Edit the new configuration. Press "Next" on the Step 1 of 2 dialog.
- In the Step 2 of 2 dialog, go to the species tab, select the first species in the middle column, hold shift, and select the last species in that column
- Add all species to the project by pressing the "Add Species>>" button
- Go to the TCEs tab
- Update the configuration for the TCE you are using, see TCE Configuration Help Page for more information.
You should now have a working SysCAD configuration file. The next step is to create a project and review the species properties.
- Create a new SysCAD project and select the newly created configuration. See Introductory Tutorial - Creating a SysCAD Project for more details.
- Once the project is open, review the species properties
- Go to Species->View Properties
- This brings up a window showing all data used for all species. More information on this window is here: Species Properties ($SDB). It is recommended to carefully review this to ensure it is correct.