SysCAD Marshal: Difference between revisions
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
These are optional. If filename is specified, then when saving and loading scenarios, SysCAD Marshal will save and recover all the OPC tag values listed. The "filename.mtl" is a text file (extension mtl Marshal Tag List) which is a list of all the OPC tags to be saved/recovered. The ability to set all the saved OPC tag values in the OPC Server (during load scenario) will depend on whether the OPC Server supports a write of all these tags. | These are optional. If filename is specified, then when saving and loading scenarios, SysCAD Marshal will save and recover all the OPC tag values listed. The "filename.mtl" is a text file (extension mtl Marshal Tag List) which is a list of all the OPC tags to be saved/recovered. The ability to set all the saved OPC tag values in the OPC Server (during load scenario) will depend on whether the OPC Server supports a write of all these tags. | ||
<nowiki>The file filename.MTL has the following format: | <nowiki> | ||
The file filename.MTL has the following format: | |||
Tag , Type , Access | Tag , Type , Access | ||
<<<SOFTLGX1>>> | <<<SOFTLGX1>>> | ||
| Line 106: | Line 107: | ||
[PLC101A]CNB_JC15_CV10_HIC01:I.Data[20] | [PLC101A]CNB_JC15_CV10_HIC01:I.Data[20] | ||
[PLC101A]CNB_JC15_CV10_HIC01:I.Data[21] | [PLC101A]CNB_JC15_CV10_HIC01:I.Data[21] | ||
...</nowiki> | ... | ||
</nowiki> | |||
Where <<<SOFTLGX1>>> is the name of ??? and each subsequent line is the tag of a PLC entry to be saved and restored during scenario save/restore. | Where <<<SOFTLGX1>>> is the name of ??? and each subsequent line is the tag of a PLC entry to be saved and restored during scenario save/restore. | ||
Revision as of 08:30, 7 February 2012
Navigation: User Guide -> SysCAD Marshal
Introduction
SysCAD Marshal is an OPC client, allowing easy connection to OPC servers. SysCAD Dynamic projects can connect to any number of OPC servers that may be on the same PC or on other PC's on the network.
Getting Started with OPC Server and Client
Before trying to connect to SysCAD by configuring SysCAD Marshal, it is worth completing two steps:
- Do you have an OPC Server installed and configured? This is the OPC Server that Marshal will ultimately connect to. Perhaps create a few dummy OPC tags in the server of different data types (including read/write) for testing in next step.
- Using any simple OPC Client test software, ensure that you can connect to the OPC Server. When connected, ensure that you can read and write to tags. Test this for "digital" and "analog" OPC tag types. If you have an OPC Client tool that you use for testing from the same supplier as the OPC Server, it is good to use this; but then it is a very good idea to repeat the tests with an independent 3rd party OPC Client tool.
If a 3rd party OPC Client can see and read/write to your OPC Server, then it is almost certain that SysCAD OPC Client (ie Marshal) will connect and communicate.
The OPC Server does not necessarily have to be on the same PC as SysCAD. If the OPC Server and Client are going to be on different machines on the network, it is important to test an independent OPC Client across the network. It is still a good idea to test these on the same PC first; and then test from a connected PC. Over a network, you need to ensure that DCOM user permissions are configured correctly on both machines. There are a number of web sites describing this process.
When the OPC Server is installed, it is likely it will have installed the OPC Core Components (version 2.0 or newer). This is not installed with SysCAD, but a copy of the install for the OPC Core Components Redistributable is included in the ...\Setup\OPC Setup folder. You can install this directly, which may be necessary if SysCAD Marshal gives error messages such as "Error connecting to OPC 2.0 Server Browser".
Getting Started with Marshal (as OPC Client)
To use the IO Marshal option in SysCAD, the user must first have the following prerequisite.
- Use a simple OPC Client test application to ensure the OPC Server operates correctly as described in [Getting Started with OPC Server and Client].
- The Marshal (OPC Client) License Option must be enabled.
- The user must create a SysCAD Marshal (.scm) file. This simple text file can be stored in the project folder.
- The user must create a IO tag list file (either in MS Access database format or Excel Table format). In this table, IO tags are created and defined for communication between the SysCAD Marshal and OPC Server(s). Note that this database must be in the same folder as the Marshal .scm configuration file.
Note: Marshal refers to the tag list as slots
To use the Marshal tag list file in a SysCAD project, the user should do the following:
- Open the SysCAD project.
- From the Menu select Project - Settings and click on the IO Connections tab.
- Please see Project Settings for a description of the available fields.
- Modifications to IO tag list can be made directly through MS Access or Excel. When adjustment to the IO table is complete, save (if necessary) and reload it into SysCAD Marshal. Note that the SysCAD project need not be closed and reloaded for this process.
SysCAD Marshal file (.scm)
A text file "xxxx.scm", the marshal configuration file, must exist in the same folder as the IO tag list (slots) file xxx.mdb (eg: ScdDrvr.mdb). The scm file is the same format as a windows INI file. Any line starting with a ';' is a comment and is ignored.
For Example: See below when editing a .scm file in a text editor (eg Notepad). This example has two OPC Servers "WinCC" and "RunSigs".
[Databases] Slots=Slots.xls CodeBlocks=CodeBlks.xls [Thread] Priority=Above_Normal DelayResolution=50 ReconnectHold=60 ReconnectItemBlk=100 [DCOM] ClassContext=LOCAL_SERVER | REMOTE_SERVER | [Scenario] TagListFile=Tags.MTL ValueSetPath= [WinCC] Node=200.200.200.101 ProgID=OPCServer.WinCC UpdateRate=100 [RunSigs] Node= ProgID=ScdIODB.OPC.1 UpdateRate=500
[Databases] section
Slots = The file name of the MS Access database or MS Excel file containing the list of slots and the configuration for each slot (tag). CodeBlocks = Optional. The file name of the MS Excel file containing the list of available code blocks.
[Thread] section
Priority=Above_Normal
DelayResolution=50
ReconnectHold=60
ReconnectItemBlk=100
[DCOM] section
ClassContext=LOCAL_SERVER | REMOTE_SERVER |
[Scenario] section
TagListFile=filename.MTL
ValueSetPath=path
These are optional. If filename is specified, then when saving and loading scenarios, SysCAD Marshal will save and recover all the OPC tag values listed. The "filename.mtl" is a text file (extension mtl Marshal Tag List) which is a list of all the OPC tags to be saved/recovered. The ability to set all the saved OPC tag values in the OPC Server (during load scenario) will depend on whether the OPC Server supports a write of all these tags.
The file filename.MTL has the following format: Tag , Type , Access <<<SOFTLGX1>>> [PLC001A]DS20_PU15_M01].DRIVE_FLTS_HIST [PLC001A]DS20_PU25_M01].DRIVE_FLTS_HIST [PLC001A]DS20_PU25_XV01_ZIC [PLC001A]DS20_PU25_XV01_ZIO <<<SOFTLGX1>>> [PLC101A]CNB_JC15_CV10_HIC01:I.Data[20] [PLC101A]CNB_JC15_CV10_HIC01:I.Data[21] ...
Where <<<SOFTLGX1>>> is the name of ??? and each subsequent line is the tag of a PLC entry to be saved and restored during scenario save/restore.
["OPC Server"] section
The user can specify any number of "OPC Server" sections and give them any names you choose. In the example above they are "WinCC" and "RunSigs". This name is used when defining the slots. Each slot (OPC tag) will use one of these defined OPC Server section names in the scdDriver field as the mechanism to associate a slot with a particular OPC Server.
Node = This field is optional, it is used when the OPC Server is located on a remote computer.
ProgID = The OPC Server Program ID. This is the same name that you see for the OPC Server when in an OPC Client you browse through a list of installed OPC Servers.
UpdateRate = Time in milliseconds.
Running SysCAD Marshal
SysCAD Marshal can be executed from within SysCAD as mentioned in Getting Started or it can be started separately without starting SysCAD. To do this, user can start up SysCAD Marshal directly from the Bin folder.
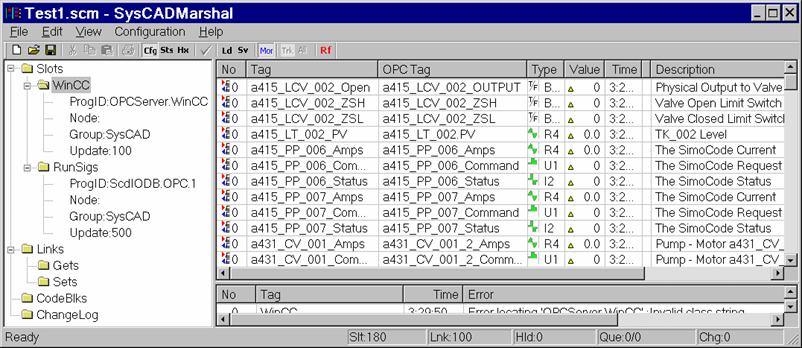
Test.scm is loaded below by SysCAD Marshal to show how the data is presented:
SysCAD Marshal Menu Options
Configuration | Delays Enabled can be used to switch on or off all timer delays for OPC tags. In other words, when not checked, ignore all delays specified in the tag list.
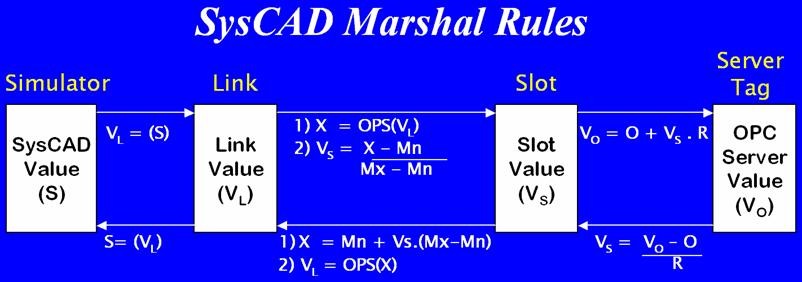
SysCAD Marshal Rules
Where:
Mn = Range Min
Mx = Range Max
R = Span Range
O = Span Offset
Slots
The SysCAD Marshal Slots table are explained in the IO Tag List (or Driver Slot) file (xxx.mdb or xxx.xls)
Note that this file can now be named freely, as long as the correct association is made in the .scm file under the [Databases] section.
Links
'Set' Means when THIS slot changes SET the tag specified by the Set
'Get' Means when the tag specified by the Get changes, GET the values and set THIS slot
For Example:When Slot a415_PP_006_Command changes
Set Cb_a415_PP_006.Command then execute the CodeBlock. Then Get the Cb_a415_PP_006.Status and Set the slot a415_PP_006_Status, which will go back to the OPC Server
Code Blocks
The SysCAD Marshal code blocks are like mini pgm text files with file extension .dcb and loaded by SysCAD Marshal. They are executed by SysCAD marshal as needed (ie on change) without the need to pass through SysCAD, so they are independent of the execution and iterations of the SysCAD model. This improves significantly the turn around time on certain signals and logic. The other advantage is that relatively complex logic or simulation can be implemented in code blocks, whereas only some simple logic expressions can be implemented in the scdConnection column.
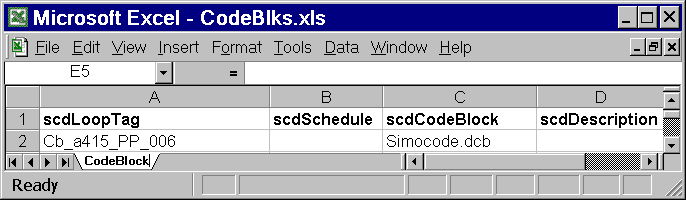
The SysCAD Marshal code blocks are managed and called from the codeblock MS Excel file. As with the slots file, this file name can be user defined as long as the correct association is made in the .scm file under the [Databases] section.
In general, SysCAD requires the following fields in the codeblock table to ensure correct and complete operation of the SysCAD Marshal.
- ScdLoopTag: This is the name of the "object" or "loop". This is the main part of the tag that can then be used in the Slots table (scdConnection column).
- scdSchedule: Not used.
- scdCodeBlock: This is the name of the corresponding code block (.dcb) text file.
- scdDescription: Optional. User may enter a description.
The actual code blocks called by the codeblock.xls are text files with the extension (.dcb), written in PGM language.
An Example of a code block "Simocode.dcb" is as follows:
- bit Run
- Long Status, Amps, Command
- IF Command == 1151
- Status = 43829
- Amps = 10
- Run = 1
- ELSE
- Status = 43825
- Amps = 0
- Run = 0
- ENDIF
- $
The variables declared in the codeblock can be referenced in the scdConnection column of the slots file by combining the scdLoopTag defined in the CodeBlocks file together with the variable in the associated code block. There may be any number of "loops" defined using the same code block file. Effectively independent instances of the "loop" or "object".
Accessing codeblock variables: For example you may have "set(Cb_a415_PP_006.Command)" to set the value of Command from an OPC tag. When the OPC tag changes, it will set Command which also causes the code block to execute. The code is executed when any value is changed. To retrieve a value from a code block you would use "get(Cb_a415_PP_006.Run)" in the scdConnection column. In the above example, the values of "Status", "Amps" and "Run" are changed based on the value of "Command". It is implied that "Command" would be set from outside the codeblock by an OPC tag or by a SysCAD flowsheet tag.
IO Tag List (or Driver Slot) file (xxx.mdb or xxx.xls)
The IO Tag list (or driver slot) file needs to be in form of an Access Database "xxx.mdb" or Excel table "xxx.xls", this file should be created by the user prior to loading into the project. (Eg, ScdDrvr.mdb.)
In general, SysCAD requires the following fields in the IO Tag List to ensure correct and complete operation of SysCAD Marshal.
- ScdLoopTag: Required field. This must be a unique tag, therefore it should be indexed with no duplicates. Spaces and most special characters are not allowed (same rules as SysCAD tags).
- ScdConnection: Optional field. Connection information with SysCAD tags. See ScdConnection for valid formats.
- ScdTyp: Required field. See ScdTyp for more information.
- ScdDriver: Required field. Full address of slot. User must specify the OPC Server section name (as defined in the .scm file) and corresponding OPC tag in the server. Syntax is OPC(server_name, OPC tag). Eg. OPC(WinCC, CV1_speed).
- ScdModifier: Extra information on the raw or digital value sent or received by the driver. Such as the bit number for a digital slot or the span and offset for an analogue slot. See ScdModifier.
- ScdRange: Sets the minimum and maximum number for an analogue slot. See ScdRange.
- ScdFilter: See ScdFilter for more information.
- ScdCompression: See ScdCompression for more information.
- ScdConversion: Engineering unit for analogue slots. See ScdConversion for more information.
- ScdDescription: This is the driver tag description. The description will appear in the Description Column in Marshal.
- ScdArchive: See ScdArchive for more information.
All of the fields listed above should be included as column headings in the IO database design. The only fields that are required to be filled in for each variable are ScdLoopTag, ScdTyp and ScdDriver.
Please note that other fields are allowed in the table, therefore, the user can add in any other information that may be useful to them, but SysCAD will only use the above-mentioned fields.
ScdConnection
This is the field that sets up the connection between SysCAD and the driver, so that information can be transferred between the two. As a general rule, all GET functions should have WRITE access enabled and SET function should have READ access enabled.
Multiple functions can be entered in this field separated by commas, and a single function can contain multi parts separated by colons. For this please see the sub heading under connection function examples.
Valid functions for transferring information from SysCAD to Marshal are:
NOTE: All Get functions should have write access enabled
- Get(tag) : transfers the value of the specified tag to the OPC Server (ie Device/Driver/PLC/etc) after each iteration only if it changes.
- For example: Get(TNK_1.Lvl (%))
- Get(tag, DelayTime), Get(tag, DelayTime, DelayTime2) - transfers the value of the specified tag to the OPC Server after delay specified in milli-seconds. The delay time is an optional parameter. The second, optional parameter DelayTime2, can only be used for bit slots. When the tag changes to 0 (false) the specified OPC Server tag is changed after a DelayTime milli-seconds, and when the tag changes to 1 (true) the specified OPC Server tag is changed after DelayTime2 milli-seconds.
- GetDelay(tag, DelayTime, RandomDelayTime) - transfers the value of the specified tag to the OPC Server after a delay specified in milli-seconds. The parameter RandomDelayTime is optional. If this is not specified, the delay time is fixed at the value specified for the parameter DelayTime. If RandomDelayTime is specified, the total delay time is calculated as DelayTime plus a random number between zero and RandomDelayTime where the probability of any number in this range is equal (ie a "flat" distribution).
- For example: Get(TNK_1.Lvl (%), 1000, 500)
- GetCmp(tag, comparison operator, value) : Only valid for a bit data type. Transfers 0 or 1 to the OPC Server depending on the result of the expression generated by the parameters. The SI units as defined in the conversion file MUST be used.
- Examples:
- GetCmp(Tnk_1.Lvl (%),<,1) sets the driver slot bit to 1 if the tank level is less than 1% full.
- GetCmp(P_1.T (C),>,100) returns 1 if the temperature in the pipe exceeds 100 °C.
- GetAbs(tag) : Only valid for a float data type. Transfers the absolute value of the tag.
- Examples:
- GetAbs(GC_1.dT) ;returns the absolute temperature change.
- GetRev(tag, offset) : Only valid for a float data type. Transfers the reverse value of the tag plus the offset value.
- Examples:
- GetRev(GC_1.ReqChange,10) ;If reqChange is 100, then the value returned will be 110.
- GetSqr(Tag, multiplier) or GetSqr(tag, multiplier, [minI], [maxI]) : Only valid for a float data type. Returns the square of (tag value times by the multiplier). The ScdRange field must be specified.
- Examples - GC_1.value1 = 100:
- GetSqr(GC_1.value1,0.2) ;returns 400. Thus (10*0.2)^2
- GetSqr(GC_1.value1,1,0,1000) ; returns 10. Thus (100*1)^2/(1000-0)
- GetSqrt(tag, multiplier) or GetSqrt(tag, multiplier, [minI], [maxI]) : Only valid for a float data type. Returns the square root of tag value, then times by the multiplier. The ScdRange field must be specified.
- Examples - GC_1.value1 = 100:
- GetSqrt (GC_1.value1,2) ;returns 20.
- GetSqrt(GC_1.value1,2,0,1000) ; returns 632.45.
- GetProfile(Tag, FileName, [Reverse]) - This function allows the user to fetch a corresponding number from a correlation using interpolation, thus this data file must contain at least two data points, thus (x1,y1) and (x2,y2). The format of this file must be a text or csv file and the first line of the file must contain any combination of the following ABS, SCL, SCL% or Contronic.
[Reverse] = 0 for 1st column in text file is X value or 1 for 1st column in text file is Y value.
Function will return: File:User Guide image390.gif
Valid functions for transferring information from Marshal to SysCAD are:
NOTE: All Set functions should have read access enabled
- Set(tag) - the specified tag is changed immediately.
- Set(tag, DelayTime) - the specified tag is changed after delay specified in milli-seconds. The delay time is an optional parameter.
- Set(tag, DelayTime, DelayTime2) - this option can only be used for bit slots. When the driver tag changes to 0 (false) the specified tag is changed after a DelayTime milli-seconds, and when the driver tag changes to 1 (true) the specified tag is changed after DelayTime2 milli-seconds.
- SetInv(tag), SetInv(tag, DelayTime) and SetInv(tag, DelayTime, DelayTime2) operate as described above except the output is inversed (ie performs a bitwise not).
- SetDelay(tag, DelayTime, RandomDelayTime) - the specified tag is changed after a delay specified in milli-seconds. The parameter RandomDelayTime is optional. If this is not specified, the delay time is fixed at the value specified for the parameter DelayTime. If RandomDelayTime is specified, the total delay time is calculated as DelayTime plus a random number between zero and RandomDelayTime where the probability of any number in this range is equal (ie a "flat" distribution).
Changes based on rising and falling edges can be made by setting one of the delay times to INF (infinity).
- Example: Set(Pump_3.Speed.State, INF, 0) will switch the pump on when the slot changes from 0 to 1 (rising edge) but will do nothing when the slot changes from 1 to 0 (falling edge).
- Note: Forcing and Ignoring do not necessarily affect the Sets described here. They are implemented at a low level in the driver to supply a fast 'turn-around' time.
Connection function examples:
Example 1) Multiple functions.
We have the following flowrate and valve %open data:
| Flowrate | Valve%Open | ||
| 50 | 10 | ||
| 70 | 25 | ||
| 90 | 40 | ||
| 120 | 60 | ||
| 150 | 80 | ||
| 180 | 100 |
What we want to do is based on the flowrate measurement change the valve setting accordingly. To do so, we can do the following:
1. Create a text file called "flow.txt" or a comma-delimited file called "flow.csv" containing the above data in the following format:
ABS SCL%
2. In the ScdDrvr table, select the Scdloop tag that is going to send the signal to the valve, in the connection column, type in the following:
GetProfile("P_5.Qm (t/h)", "flow.txt", 0), Set("VLV_1.Posn.Reqd (%)", 500)
The above command will do the following when loaded in SysCAD:
1. Get tag value for P_5.Qm in t/h. Let's say this value returns 100.
2. From the flow.txt, SysCAD uses interpolation to calculate
Y = 40 + (60-40) * (100-90)/(120-90) = 46.67. 3. The valve %opening in SysCAD is set to 46.67 after 500ms delay.
Example 2) Function with multiple parts.
Get("S612-1.NQv (Nm^3/h)"):Rng(0,10000):Sqr(0.001)
ScdTyp
The data type, read/write access and other options are specified in this column. The options are separated by commas and may be in any sequence.
Data types - A data type MUST be specified:
- b : (bit 0 or 1)
- u8 : (unsigned 8bit number char 0 to 255)
- u16 : (unsigned 16bit number word 0 to 65535)
- u32 : (unsigned 32bit number dword 0 to)
- i8 : (signed 8bit integer byte -128 to 127)
- i16 : (signed 16bit integer short -32768 to 32767)
- i32 : (signed 32bit integer long -2147483648 to 2147483647)
- f16 : (3 significant digits, signed 16bit floating point number unique to SysCAD flt16 -262144 to)
- f32 : (7 significant digits, signed 32bit floating point number float 3.4E+/-38)
- f64 : (15 significant digits, signed 64bit floating point number - double 1.7E+/-308)
IO Type (Read/write options) - A IO type MUST be specified:
- ro : SysCAD has read-only access to the driver slot. (This means the driver file sends value to SysCAD. Therefore Set functions can be used.)
- wo : SysCAD has write-only access to the driver slot. (This means the driver file receives value from SysCAD. Therefore Get functions can be used.)
- rw : SysCAD has read-write access to the driver slot. (This means the driver file can send or receive values to or from SysCAD, both Get and Set functions can be used, delays should be used to give it time to process data.)
Other options:
- h : SysCAD automatically records that tag in the historian.
- l : Local slot.
The value of that slot is saved and restored when saving and loading SysCAD projects. An initial value for a tag can be specified by using l=value. The initial value is only used the first time the slot is loaded in a project. The value must be in the units specified in the Conversion column.
Note that a local slot's access is assumed to be write-only (wo) regardless of the read/write options specified. Note that local slot values are restored when a project is loaded, they are NOT restored when the driver is switched off then back on!
- f : Enable forces.
The forcing capability for that slot is enabled. A force value may be specified by using f=value. The value must be in the units specified in the Conversion column.
- ir : Ignore reads. Enable ignoring capability for reads.
- iw : Ignore writes. Enable ignoring capability for writes.
- irw : Ignore reads and writes. Enable ignoring capability for reads and writes.
NOTE
The data type chosen must be able to store the full range of values in their SI unit. For example a slot using f16 for range 0 to 5000 in tons corresponds to values of 0 to kg in the SI units, this will result in incorrect values (overflow) because this exceeds the maximum value for the f16 data type.
ScdModifier
How the driver value is modified to get the tag value. The modifier used must relate to the data type in the Type column. The modifier (together with the range) converts a digital integer value to the data type specified in the Type column.
For example a 4 to 20 milliAmp analog signal is received as a raw digital value in the range 0 to 4095. This digital value is then mapped to a value using the specified range.
- Span (2 parameters - span and offset) eg Span(3840, 128), Span(4095, 0)
- Mask (1 parameter - hex bit mask) eg Mask(0xffff)
- Bit (1 parameter - bit number from 1 to 16 or 0 to 15) eg Bit(5)
- None (0 parameters) eg None()
ScdRange
This indicates the value's range. It has two parameters Min and Max that correspond to the minimum and maximum driver values. Eg, Range(0,1500). The units used must correspond to the Conversion column.
Typically an analog slot uses the span modifier as a full range. Check the driver documentation to see (1) how values are translated from engineering units to digital raw values used by the driver and back; and (2) if clamping is enabled when a value exceeds the range (ie how are values above and below the range handled).
ScdFilter
This is the signal processing algorithm(s) to be implemented on the input data to SysCAD from the field. These are used if a tag is being recorded in the historian. Window and First can be used together by separating them with a comma. The units used must correspond to the Conversion column. See section on Historian Filtering.
For example, a window filter is used to have a smoothing effect on analog inputs.
- None()
- Window(length)
- First(Tau, Period, Delta)
ScdCompression
The type of data compression to be performed by the historian. The units used must correspond to the Conversion column. See section on Historian data compression.
- None()
- Box(Delta)
- ABox(DeltaLo, DeltaHi, NoRec, NoNotRec, Change)
ScdConversion
The dimension/group and engineering unit for the value used. These must be valid and in the format Dimension(unit). See section on Cnvs Table (Engineering Units Conversion).
eg P(kPag), T(dC), Frac(%)
ScdArchive
This field is optional and will only be valid if the Archive option in SysCAD is switched on. It allows the user to add any driver slot tags to the Archive, an example is:
Table(Avg,Min,Max,Cnt)
The above example will add the average, min, max and count values to the Table in ScdArchive.mdb. For more information, please refer see Archive Options.
Adding data from Driver Slot File
Driver slot tags can be added to the archive database by entering the command in the ScdArchive field. Using the same example as in the previous heading, we will add the following to the ScdDrvr.mdb - ScdDrvr table (see IO Tag List (or Driver Slot) file (xxx.mdb or xxx.xls) for more information):
ScdLoopTag ... ScdArchive
B3:100 ... RawData(Cnt,Avg,Min,Max)
The above example adds the B3:100 count, Average, Minimum and Maximum values to the ScdArchive.mdb - RawData Table.
Trending SysCAD Marshal Driver Tags
The marshal IO tags can be shown on the Trend window as normal. The full tags would be MarshalTag.Slot.Field or MarshalTag.Link.Field. Valid fields are Value, HoldValue, Hold, Type, Changes and Ignored.