Stream Properties using Standard Method: Difference between revisions
Peter.Marsh (talk | contribs) |
Ab.Rijkeboer (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
The C<sub>p</sub> values for each individual component are calculated at the specified temperature, in K, using the above equations, and Enthalpies ('Hs') are calculated by integrating the above equations from Reference temperature 273.15K to the specified temperature. The results of these calculations are presented in Table 3. (Note that since the reference temperature of 273.15K is less than Ts (Start Temperature) of | The C<sub>p</sub> values for each individual component are calculated at the specified temperature, in K, using the above equations, and Enthalpies ('Hs') are calculated by integrating the above equations from Reference temperature 273.15K to the specified temperature. The results of these calculations are presented in Table 3. (Note that since the reference temperature of 273.15K is less than Ts (Start Temperature) of 298.15K, to calculate Hs the Cp at 298.15K will be multiplied by (298.15-273.15).See [[Species Table - Thermodynamic Data#Heat Capacity (Cp)|Heat Capacity (Cp)]] for more information.) | ||
Revision as of 11:26, 5 December 2013
Navigation: Models -> Examples -> Model Examples
Introduction
Given the following stream make up at 25°C and atmospheric pressure, stream properties are calculated in SysCAD using the Standard specie model, primarily a mass weighted mean method. These calculations are illustrated using the example below:
Table 1 Stream Make Up
| Stream Make Up | Mass Flow | Mass Frac | Mole Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| kg/h | wt Frac | kmol/h | |
| CaCO3(s) | 200.00 | 0.20 | 1.998 |
| SiO2(s) | 300.00 | 0.30 | 4.993 |
| H2O(l) | 400.00 | 0.40 | 22.203 |
| H2SO4(aq) | 80.00 | 0.08 | 0.816 |
| CO2(g) | 10.00 | 0.01 | 0.227 |
| N2(g) | 10.00 | 0.01 | 0.357 |
| Total | 1000.00 | 1.00 | 30.594 |
Table 2 Component Data entered into the SysCAD Specie Database.
| Component | Density (kg/m3 | Hf at 25 (J/mol) | Cp Equation (kJ/kmol.K) | Temp Range (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaCO3(s) | 2650 | -1208352 | HTE_Cp(-9122, 23.8351, 3.2146, 5.1569) | 298 - 1200 |
| SiO2(s) | 2650 | -911550 | HTE_Cp(-8654, 19.1651, -0.5456, 8.8977) | 298 - 2000 |
| H2SO4(aq) | 1841 | -886513 | HTE_Cp(-7762, 19.1799, 23.2471, -0.0679) | 298 - 500 |
| CO2(g) | 1.8 | -393505.213 | Poly_Cp(19.7961, 0.07344, -5.600221e-05, 1.71541e-08) | 298.15 - 1000 |
| N2(g) | 1.15 | 0 | Poly_Cp(31.1513, -0.0135659, 2.67968e-05, -1.16817e-08) | 298 - 1000 |
Note:
Properties for H2O are NOT entered by the user - these values are calculated within SysCAD. See Water and Steam Properties.
From Heat Capacity (Cp), we will find the Cp equation formats for the HTE_Cp and Poly_Cp as follows:
HTE_Cp(a,b,c,d) :
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{C_p = 4.186*\left (b+2*c.10^{-3}*T-\frac{d.10^5}{T^2} \right )}} }[/math]
Poly_Cp(a,b,c,d):
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{C_p = a+b*T+c*T^2+d*T^3}} }[/math]
The Cp values for each individual component are calculated at the specified temperature, in K, using the above equations, and Enthalpies ('Hs') are calculated by integrating the above equations from Reference temperature 273.15K to the specified temperature. The results of these calculations are presented in Table 3. (Note that since the reference temperature of 273.15K is less than Ts (Start Temperature) of 298.15K, to calculate Hs the Cp at 298.15K will be multiplied by (298.15-273.15).See Heat Capacity (Cp) for more information.)
Table 3 Component Properties Summary at 25°C and 1 Atmospheric Pressure
| Component Properties |
MW kg/kgmol |
Density kg/m3 |
Hf at 25°C kJ/kg |
Hs kJ/kg |
Cp kJ/kg.C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaCO3(s) | 100.09 | 2650.00 | -12072.99 | 20.85 | 0.83 |
| SiO2(s) | 60.08 | 2650.00 | -15171.18 | 15.36 | 0.62 |
| H2O(l) | 18.02 | 997.04 | -15865.97 | 104.87 | 4.18 |
| H2SO4(aq) | 98.08 | 1841.00 | -9038.72 | 35.33 | 1.41 |
| CO2(g) | 44.01 | 1.80 | -8941.31 | 21.11 | 0.84 |
| N2(g) | 28.01 | 1.15 | 0.00 | 26.04 | 1.04 |
Notes:
- The user specifies properties of individual compounds in the SysCAD specie database.
- Hs and Cp values are derived from the Cp equations.
- The individual component properties at different Temperature and Pressures can be obtained via the menu command View -- Species Data.
Table 4 Stream Properties Summary
| 0°C | 25°C, 1 atm | 50°C, 1 atm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stream Properties | MW | Density | Hs | Hf | Hs | Cp | Hf | Hs | Cp |
| kg/kgmol | kg/m3 | kJ/kg | kJ/kg | kJ/kg | kJ/kg.C | kJ/kg | kJ/kg | kJ/kg.C | |
| Total | 32.69 | 67.00 | 0 | -14124.85 | 54.02 | 2.16 | -14070.42 | 108.46 | 2.20 |
| Solid Phase | 71.52 | 2650.00 | 0 | - | 17.56 | 0.70 | - | 36.15 | 0.78 |
| Liquid Phase | 20.85 | 1079.53 | 0 | - | 93.28 | 3.72 | - | 186.34 | 3.73 |
| Vapour Phase | 34.24 | 1.40 | 0 | - | 23.58 | 0.94 | - | 47.31 | 0.96 |
| Slurry (Sol + Liq) | 32.66 | 1547.40 | 0 | - | 54.65 | 2.18 | - | 109.71 | 2.22 |
The methods used to calculate these values are shown in the following headings:
Stream Molecular Weight
[math]\displaystyle{ Stream Molecular Weight = \frac{\sum{m_i}}{\sum{n_i}} }[/math]
where: mi = mass of individual component
- and ni = mole of individual component
So for the above example:
[math]\displaystyle{ Stream Molecular Weight = \frac{1000kg}{30.594kgmoles} = 32.69kg/kgmol }[/math]
Note:
SysCAD uses the atomic weight of the elements and the compound definition in the Specie Database to calculate the Molecular weight of each compound.
Stream Density
The Stream Density is calculated as:
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{Total\ mass}{Total\ volume} = \frac{\sum{m_i}}{\sum{\frac{m_i}{p_i}}} }[/math]
where: mi = mass of individual component
- ρi = density of individual component
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{Stream Density = 1000 / (200/2650 + 300/2650 + 400/997.04 + 80/1841 + 10/1.80 + 10/1.15) = 67.00 kg/m^3}} }[/math]
Like wise,
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{Solid Density = Total Solid Mass / Total Solid Volume = 500 / (200/2650 + 300/2650) = 2650 kg/m^2}} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{Liquid Density = Total Liquid Mass / Total Liquid Volume = 1079.53 kg/m^2}} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{Vapour Density = Total Vapour Mass / Total Vapour Volume = 1.40 kg/m^2}} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{Slurry Density = Total (Solid + Liquid) Mass / Total (Solid + Liquid) Volume = 1547.40 kg/m^2}} }[/math]
See also: Density and Volume display for mixtures
For solution density calculations requiring correction functions, please see Density Correction for Solutions & Data Fitting.
Stream Enthalpy values (Hs)
Stream Enthalpy values are calculated using the mass weighted mean method. Using values in Table 3 Component Properties Summary, we have:
| Hs @T | = | Stream Enthalpy (Heat Content) |
| = | [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_i * Hs_i }} }[/math] | |
| where mfi and Hsi are mass fraction and enthalpy of individual components respectively | ||
| = | [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ 0.2*20.85 + 0.3*15.36 + 0.4*104.87 + 0.08*35.33 + 0.01*21.11 + 0.01*26.04}} }[/math] | |
| = | [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ 54.02 kJ/kg}} }[/math] | |
| SmsHs @T | = Solids Enthalpy |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_{i \ solids} * Hs_i = 0.2/0.5*20.85 + 0.3/0.5*15.36 = 17.56 kJ/kg }} }[/math] | |
| where mfi solids is the mass fraction of solids in the solid phase |
| LmsHs @T | = Liquid Enthalpy |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_{i \ liquids} * Hs_i = 0.4/0.48*104.87 + 0.08/0.48*35.33 = 93.28 kJ/kg }} }[/math] | |
| where mfi liquids is the mass fraction of liquids in the liquid phase |
| VmsHs @T | = Vapour Enthalpy |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_{i \ vapour} * Hs_i = 0.01/0.02*21.11 + 0.01/0.02*26.04 = 23.58 kJ/kg }} }[/math] | |
| where mfi vapour is the mass fraction of vapour in the vapour phase |
| SLmsHs @T | = Slurry Enthalpy |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_{i \ slurry} * Hs_i }} }[/math] | |
| where mfi slurry is the mass fraction of liquid/solid in the slurry (liquid+solid) phase | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{0.2/0.98*20.85 + 0.3/0.98*15.36 + 0.4/0.98*104.87 + 0.08/0.98*35.33}} }[/math] | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{54.65 kJ/kg}} }[/math] |
Stream Specific Heat values (Cp)
Stream Specific Heat values are calculated using the mass weighted mean method. Using values in Table 3 Component Properties Summary, we have:
| Cp @T | = Stream Cp |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_i * Cp_i}} }[/math] | |
| where mfi and Cpi are mass fraction and Cp of individual components respectively | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{0.2*0.83 + 0.3*0.62 + 0.4*4.18 + 0.08*1.41 + 0.01*0.84 + 0.01*1.04 }} }[/math] | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{2.16 kJ/kg.C}} }[/math] |
| SmsCp @T | = Solids Cp |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_{i \ solids} * Cp_i = 0.2/0.5*0.83 + 0.3/0.5*0.62 = 0.70 kJ/kg.C }} }[/math] | |
| where mfi solids is the mass fraction of solids in the solid phase |
| LmsCp @T | = Liquid Cp |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_{i \ liquids} * Cp_i = 0.4/0.48*4.18 + 0.08/0.48*1.41 = 3.72 kJ/kg.C }} }[/math] | |
| where mfi liquids is the mass fraction of liquids in the liquid phase |
| VmsCp @T | = Vapour Cp |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_{i \ vapour} * Cp_i = 0.01/0.02*0.84 + 0.01/0.02*1.04 = 0.94 kJ/kg.C}} }[/math] | |
| where mfi vapour is the mass fraction of vapour in the vapour phase |
| SLmsCp @T | = Slurry Cp |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum mf_{i \ slurry} * Cp_i }} }[/math] | |
| where mfi slurry is the mass fraction of liquid/solid in the slurry (liquid+solid) phase | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{0.2/0.98*0.83 + 0.3/0.98*0.62 + 0.4/0.98*4.18 + 0.08/0.98*1.41}} }[/math] | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{2.18 kJ/kg.C}} }[/math] |
Stream Heat of Formation values (Hf)
Consider the stream is at 50°C; the stream enthalpy calculations are as follows:
Stream Heat of Formation values are calculated using the mass weighted mean method. Generally, the Heat of Formation data available are at 25°C. Thus, using these values, stream Hf at 25°C is calculated.
From Table 3 Component Properties Summary, we have:
| Stream Hf25°C | = [math]\displaystyle{ \sum mf_i * H_{f \ i}^{25} }[/math]
| |||
| [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{= 0.2*-12072.99 + 0.3*-15171.18 + 0.4*-15865.97 + 0.08*-9038.72 + 0.01*-8941.31 + 0.01*0}} }[/math] | ||||
| [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{= -14124.85 kJ/kg}} }[/math] |
| Stream Hf 0°C | = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ H_f^{25} - \sum \int\limits_{0}^{25}Cp_i.dT}} }[/math] |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{H_f 25^{\circ}C - (Hs 25^{\circ}C- Hs 0^{\circ}C)}} }[/math] | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{-14124.85 - (54.02 - 0)}} }[/math] (See Table 4 Stream Properties Summary) | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{-14178.88 kJ/kg}} }[/math] |
| Stream Hf 50°C | = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ H_f^0 + \sum \int\limits_{0}^{50}Cp_i.dT}} }[/math] |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{H_f 0^{\circ}C + (Hs 50^{\circ}C - Hs 0^{\circ}C)}} }[/math] | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{-14178.88 + (108.46 - 0)}} }[/math] (See Table 4 Stream Properties Summary) | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{-14070.42 kJ/kg}} }[/math] |
Enthalpy Change (Hs) and (Hz)
Hs is the enthalpy change (excluding phase change) from 0°C to current temperature.
| Stream Hs 50°C | = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ \sum \int\limits_{0}^{50}Cp_i.dT }} }[/math] |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{(Hs 50^{\circ}C - Hs 0^{\circ}C)}} }[/math] | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{108.46 kJ/kg}} }[/math] (See Table 4 Stream Properties Summary) |
Hz is the enthalpy change (including phase change) from 0°C to current temperature.
| Stream Hz 50°C | = Net Enthalpy @ temperature |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{ H_{phase \ change} + \sum \int\limits_{0}^{50}Cp_i.dT}} }[/math] | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{(H final phase - H original phase) 0^{\circ}C + (Hs 50^{\circ}C - Hs 0^{\circ}C)}} }[/math] | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{0 + (108.46 - 0)}} }[/math] (See Table 4 Stream Properties Summary) | |
| = [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{108.46 kJ/kg}} }[/math] (Note this example contains no phase change) |
Note: For compounds without phase change, you will find that Hs@T = Hz@T. However, for streams involving Steam/Water, where it has [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{H_lg = 2501\ at\ 0^{\circ}C}} }[/math] & Sat. Pressure, these two terms will not be equal. See Examples on calculating Energy change around a unit for more details.
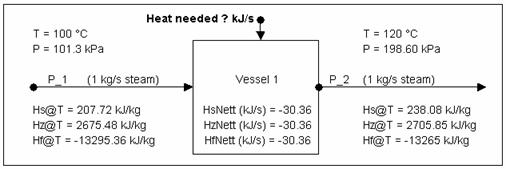
Calculating Energy change around a unit
Calculating Energy change around a unit without phase change
The above is a "summary" of information you can obtain from SysCAD.
Now to check the numbers using the steam tables[#_ftn1 [1]]:
- At [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{100 ^{\circ}C\ at\ sat. P, H_g = 2675.572 kJ/kg}} }[/math]
- At [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{120 ^{\circ}C\ at\ sat. P, H_g = 2705.9342 kJ/kg}} }[/math]
Thus energy required to heat up the steam for 20°C is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\mathit{1 kg/s * (2705.9342 - 2675.572) kJ/kg = 30.3622 kJ/s}} }[/math] (answer = to that obtained from SysCAD.)
As demonstrated by the above example, you can use Hs (sensible heat), Hz (enthalpy) or Hf (heat of formation) values to work out the energy required to raise the stream by 20°C. It is whatever you are comfortable with.