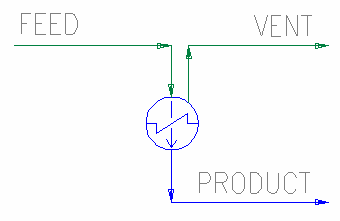
Simple Condenser
Navigation: Models ➔ Energy Transfer Models ➔ Simple Condenser
| Flash Tank | Evaporator | Falling Film Evaporator | Shell&Tube Heat Exchanger | Simple Heat Exchanger | Barometric Condenser | Direct Contact Heater | Simple Heater | Simple Evaporator | Simple Condenser |
|---|
General Description
The Simple Condenser is a generic "heat exchanger" model without regards to its cooling media or equipment size. It can provide estimates of the Duty required to condense an amount of material, or alternatively, determine the amount of condensation for a given duty or temperature.
Diagram
The diagram shows the default drawing of the Simple Condenser, with all the possible connecting streams.
The physical location of the connections is not important; the user may connect the streams to any position on the drawing.
Inputs and Outputs
| Label | Required Optional |
Input Output |
Number of Connections | Description | |
| Min | Max | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed | Required | In | 1 | 10 | Input stream to Simple Condenser. |
| Product | Required | Out | 1 | 1 | Output stream from Simple Condenser. If Vent is not present, then this will contain the condensate, non-condensed vapours and any non-condensable gases. |
| Vent | Optional | Out | 0 | 1 | Venting of gases from Simple Condenser. This may contain both non-condensed vapours and non-condensable gases. |
Behaviour when Model is OFF
If the user disables the unit, by un-ticking the On tick box, then the following actions occur:
- The Feed stream will flow straight out of the Product stream with no change in composition;
So basically, the unit will be 'bypassed' without the user having to change any connections.
Model Theory
This model is used for simple condensation, where the cooling media is not simulated but the energy from condensation is removed to keep the contents at the saturation temperature. The saturation temperature of the condensing species is based its partial pressure in the mixture, not the total pressure of the mixture.
The Simple Condenser can be configured as part of the flash train, where the steam feed to the unit can be demanded from another unit such as a flash tank based on the duty requirements.
The following methods for specifying the Condenser are available for single component condensation (Eg H2O(g) or NH3(g)):
- Fixed Duty or Duty Tag - All of the condensing species in the feed will be fully condensed, if sufficient duty is available.
- The duty methods can be configured as part of the flash train, where the steam demand can be calculated and passed on to the upstream equipment based on the required duty.
- If the demand connection is set to manual, then the duty will be applied sequentially to:
- Reduce the feed temperature to the saturation temperature (if the mixture is superheated), based on partial pressure
- Condense the condensing species
- Subcool the condensate
- Depending on the duty specified, the condensing species may be cooled, fully or partially condensed, and subcooled.
- Product Temperature - The user specifies the desired outlet temperature. If it is above the saturation temperature, then no condensation will occur. If it is at or below the saturation temperature, then all of the condensing species will be condensed.
- Saturated Temperature - The feed is heated or cooled to the saturation temperature with no condensation occurring.
- Condense All - All of the condensing species in the feed will be fully condensed. Please see assumption/limitation 4 below regarding non-condensables.
- Mass Condensed or Mass Condensed Tag - The maximum amount (mass flow) to be condensed is specified by the user or set equal to a tag.
- Fraction Condensed - The user can specify the fraction of the condensing species to be condensed.
- Bypass to Vent - Only available if a vent is connected and only relevant if feed contains some non-condensable gases. This method allows the user to specify a relative humidity in the vent stream. A fraction of the feed will be bypassed to the vent to achieve this. The remaining condensing species will be fully condensed. All non-condensables (both those bypassed and those not bypassed) will go to the vent.
Assumptions and Limitations
- The condenser unit will condense the contents to the saturation temperature based on the partial pressure, so inlet pressure and entry pressure loss of the feed is important and the user should make sure the pressure is set correctly.
- The pressure of the unit will be set at the Lowest Pressure of all the feed streams less the Entry Pressure Loss.
- The simple condenser can condense ONE single component (species) only. It cannot handle multi-component condensation.
- All feeds of the condensing species may be condensed. The amount of condensation depends on the method chosen and parameters set by the user.
- If the vapour enters the unit above the saturation temperature, it will have to be cooled to the saturation temperature before being condensed.
- With most methods, the condensate leaves the unit at the saturation temperature, i.e. there is no further cooling of the liquid. If one of the Duty methods is used and enough duty is supplied to condense all the condensing species, then subcooling of the liquid can occur, up to the maximum subcooling temperature limit.
- If non-condensables are present in the feed, and the Vent stream is present, then the non-condensables will be sent to the vent. If the vent is not present, then all contents will be sent to the product stream.
- If non-condensables are present in the feed, the Saturation Temperature changes as vapour is condensed.
- For simple methods where the user sets the amount of condensation, the outlet temperature is set to SatT@PP in the feed stream.
- For duty methods, the outlet temperature is set such that the relative humidity of the gas stream is 100% (=SatT@PP in outlet stream).
- For the Product Temperature method, the outlet temperature is set by the user and the model adjusts the amount of condensation so that the relative humidity of the gas stream is 100% (=SatT@PP in outlet stream).
- For the Bypass to Vent method, the condensate temperature is set to SatT@PP in the feed stream and the temperature of the Vent stream is determined by energy balance.
- For the duty methods with no demand connection (manual), the user specified duty may not match the condensing duty (based on fully condensing of the feed condensing species). If it is less, then condensation will be partial. If it is too much, then subcooling of the condensate can occur.
- When a vent is connected, in most circumstances, the vent and product streams will be at the same temperature. The exception is if the Bypass to Vent method is used. In this case, the vent stream is likely to be hotter than the product stream.
NOTE: Condensable refers to the condensing species, set in the VLE tab. Non-condensables refers to all other vapours. For example: if the vapour mixture contains combination of H2O(g) and NH3(g), and the condensing species is set to H2O(g), then H2O(g) will be condensed, while NH3(g) will be treated as a non-condensable and will be sent to the vent (if present).
Data Sections
The default access window consists of several sections,
- SimpleCondenser tab - This first tab contains general information relating to the unit.
- VLE - Allows the user to set the evaporation component.
- QFeed - Optional tab, visible if ShowQFeed is enabled. This and subsequent tab pages, e.g. QFeed.. and Sp, shows the properties of the combined feed stream. The tags in the QFeed tab are valid even when the ShowQFeed option is not selected.
- This page shows the properties of the combined feed after the EntryDP has been applied.
- HXCalc tab - This second optional tab allows the user to set / calculate design data for the unit based on the actual duty.
- Info tab - Contains general settings for the unit and allows the user to include documentation about the unit and create Hyperlinks to external documents.
- Links tab, contains a summary table for all the input and output streams.
- Audit tab - Contains summary information required for Mass and Energy balance. See Model Examples for enthalpy calculation Examples.
Simple Condenser Page
Unit Type: SimpleCondenser - The first tab page in the access window will have this name.
| Tag (Long/Short) | Input / Calc | Description/Calculated Variables / Options |
| Tag | Display | This name tag may be modified with the change tag option. |
| Condition | Display | OK if no errors/warnings, otherwise lists errors/warnings. |
| ConditionCount | Display | The current number of errors/warnings. If condition is OK, returns 0. |
| GeneralDescription / GenDesc | Display | This is an automatically generated description for the unit. If the user has entered text in the 'EqpDesc' field on the Info tab (see below), this will be displayed here. If this field is blank, then SysCAD will display the UnitType or SubClass. |
Requirements | ||
| On | Tick Box | If this option is deselected, the Simple Condenser will not be operational and thus inlet conditions = outlet conditions. |
Condensing Method Options | ||
| CondensingMethod / Method | Fixed Duty | This allows the user to specify the Simple Condenser duty. This method is designed to work in the demand mode, where the input vapour rate can be varied based on the specified duty and the condensing species in the feed will be fully condensed. If the demand connection is set to Manual, then the required duty may not be equal to the fully condensing duty and partial condensation or subcooling of the condensate may result. |
| Duty Tag | Same as Fixed Duty except the Duty is specified by a tag. | |
| Product Temperature | This allows the user to specify the desired product temperature. Depending on the Saturation Temperature of the feed, there may only be cooling without condensation, condensation at the saturation temperature or complete condensation with subcooling of the condensate. | |
| Saturated T | The product temperature will be equal to the saturation temperature for the condensing species (component selected on the VLE tab page). No condensation will occur. | |
| Condense All | The condensing species in the feed will be fully condensed. | |
| Mass Condensed | The user specifies the (maximum) mass of the condensing species to be condensed. | |
| Mass Condensed Tag | Same as Mass Condensed except the mass is specified by a tag. | |
| Fraction Condensed | The user specifies the fraction of the condensing species to be condensed. | |
| Bypass to Vent | Only available if a vent is connected. The user specifies a desired relative humidity in the vent stream. A portion of the feed will be bypassed to the vent to achieve this with the remainder of the condensing species being fully condensed. | |
| DutyReqd | Input | This field is only visible if Method = Fixed Duty. The required duty. If the specified Duty is too low or too high (compared to fully condensing duty), then partial condensation or subcooling of the condensate may result. |
| DutyTag | Input | This field is only visible if Method = Duty Tag. This allows the user to set the duty tag from another unit or from a side calculation. |
| DutyReqd.Meas | Calc | This field is only visible if Method = Duty Tag. It displays the actual duty value being used from the linked tag. |
| DutyFactor | Input | This field is only visible if Method = Duty Tag. The duty factor. For example: If the duty being linked is -ve, using -1 to change the duty to +ve. |
| MaxSubCoolDT | Input | This field is only visible if Method = Fixed Duty or Duty Tag and DemandConnection = None (Manual). The degrees of subcooling allowed below the saturation temperature if the duty specified exceeds what is required for full condensation of the condensing species. |
| DemandConnection (only visible for Duty Methods) |
None (Manual) | The input to the condenser is manually specified by the user. |
| General Demand | The steam supply comes from (directly or indirectly) a Feeder with Demand.on selected. | |
| Flash Train Demand | The steam supply comes from another unit such as Flash Tank. The Flash Tank - Simple Condenser will form a Flash train where the amount of flashed vapour will be varied to meet the condenser duty. | |
| TemperatureReqd / T_Reqd | Input | This field is only visible if Method = Product Temperature. The required temperature of the product stream/s. Condensation will not occur if the product temperature is above the saturation temperature of the feed. |
| CondReqd | Input | This field is only visible if Method = Mass Condensed. The required mass of the condensing species to be condensed. This will not be achieved if there is insufficient mass of the condensing species in the feed. |
| CondTag | Input | This field is only visible if Method = Mass Condensed Tag. This allows the user to set the mass condensed tag from another unit or from a side calculation. |
| CondReqd.Meas | Calc | This field is only visible if Method = Mass Condensed Tag. It displays the actual mass condensed value being used from the linked tag. |
| CondFactor | Input | This field is only visible if Method = Mass Condensed Tag. The condensation factor. For example: If the mass flow being linked is -ve, using -1 to change the mass flow to +ve. |
| FractionReqd | Input | This field is only visible if Method = Fraction Condensed. The required fraction of the condensing species to be condensed. |
Vent Stream HandlingThis section is only shown if Method = Bypass to Vent. | ||
| VentRelativeHumidity / Vent_Rh | Input | The vent relative humidity requirements. The fraction of feed that bypasses directly to the Vent stream is varied to try to achieve this. Relative Humidity = Partial Pressure of the Saturation Component (usually H2O) / Saturation Pressure of the Saturation Component at Stream Temperature * 100 |
Operating PressureThe condenser unit will fully condense the condensing species to the saturation temperature based on the partial pressure, so inlet pressure and entry pressure loss of the feed is important and the user should make sure the pressure is set correctly. | ||
| Pressure.Method | Lowest Feed | The operating pressure will be set to the lowest feed stream. |
| EntryDrop | The entry pressure loss required. The operating pressure will be set to "lowest feed stream - entry pressure loss". | |
| Required P | The required operating pressure. The entry pressure drop will be calculated and displayed in EntryDropUsed field. | |
| Atmospheric P | Pressure set to Atmospheric pressure. The entry pressure drop will be calculated and displayed in EntryDropUsed field. | |
| PressureReqd | Input | Visible with "Pressure.Method = Required P". The required operating pressure. |
| EntryPressureLoss / EntryDP | Input | Visible with "Pressure.Method = Entry Drop". The entry pressure loss required. The operating pressure will be = "lowest feed stream - entry pressure loss". |
| EntryDropUsed / DP_Used | Calc | Visible with "Pressure.Method = Required P OR Atmospheric P". The calculated entry pressure loss = lowest feed stream - pressure used. |
Options | ||
| HXSizeCalc | Tick Box | This option will add the HXCalc tab for calculations of 1) Area 2) heat transfer coefficient (HTC) or 3) log mean temperature difference (LMTD) based on the actual duty of the Simple Condenser. |
| TrackFlashSpFeed | Tick Box | Option to enable warnings if feed to unit contains solid or liquid species apart from the condensed species. |
| ShowQFeed | Tickbox | When selected, the QFeed and associated tab pages (e.g. Sp) will become visible, showing the properties of the combined feed stream. See Material Flow Section. Tags in the QFeed tab can be used for controllers (e.g.: PGM files) and reports even when this option is not selected. These tabs will show the properties of the combined feed after the EntryDP has been applied. |
Results | ||
| TemperatureIn / Ti | Calc | The inlet temperature. (A) |
| SuperHeat.TempDrop / SuperHeat.TDrop | Calc | The temperature difference between feed T and saturation temperature at partial pressure (SatT@PP), based on Total Pressure = (Lowest Pressure of all the feed streams) - EntryDP. It will show a +ve number if the feed stream is superheated. If this shows a negative number, please check the feed condition is specified correctly. (B) |
| Condensate.TempDrop / Cond.TDrop | Calc | The temperature difference between the saturation temperature at partial pressure and outlet temperature. This indicates if any subcooling of condensate has occurred, which can occur if a large duty is specified and MaxSubCoolDT > 0. (C) |
| TemperatureOut / To | Calc | The outlet temperature. (A-B-C) |
| HeatFlow | Calc | The heat flow to the condenser. This would usually be -ve, indicating that heat has been removed to cause condensation to occur. |
| MassFlow / Qm | Calc | The mass flow going through the condenser. |
| FracCondensed | Calc | The fraction of the condensing species in the feed that has been condensed. |
| VapourFracIn / Vfi | Calc | The feed vapour fraction based on total stream. |
| FlashSpInVapour /FlashSpFrac | Calc | The feed vapour fraction of the flashed species based on total vapour. For example, if feed stream contains a mixture of H2O(g) and N2(g), and the flash species is H2O(g). Then the FlashSpFrac = H2O(g) / (H2O(g) + N2(g)) * 100. |
| PressureIn / Pi | Calc | The combined feed pressure. |
| PressureOut / Po | Calc | The product stream pressure. |
| PressureChange / dP | Calc | The change in pressure. This is set by EntryDP. |
| Vent.Temperature / Vent.T | Calc | Only shown if a vent stream is connected. The vent stream temperature. The vent will be leaving the unit at the combined Feed Temperature, not the condensate temperature. |
| Vent.Pressure/ Vent.P | Calc | Only shown if a vent stream is connected. The vent stream pressure. |
Calculated Condenser Duty | ||
| Duty.Condensing | Calc | The condensing Duty of the Simple Condenser. This is the duty from fully condensing all of feed condensing species. |
| Duty.Actual | Calc | The actual Duty of the Simple Condenser. |
| The following fields are only visible if Method = Fixed Duty or Duty Tag. | ||
| Duty.Reqd | Calc | The user specified Duty for the Simple Condenser. |
| Duty.Error | Calc | The absolute difference between the Required Duty and the Actual Duty. |
| Duty.RelErr | Calc | The relative difference between the Required Duty and the Actual Duty. |
Calculated Vapour Flow Demand(This group of fields are only visible if Method = Fixed Duty or Duty Tag AND either General Demand or Flash Train Demand have been selected) | ||
| VapourFlow.Fixed | Calc | The user specified vapour flow to condenser. This normally is a result of feed stream demand connection being set to manual, or if there are more than one vapour feed streams. (A) |
| VapourFlow.Reqd | Calc | The calculated vapour flow to meet the condenser requirements. This is the calculated amount based on the user specified duty, less any fixed vapour flow to the condenser. When the heater is not in GeneralDemand or FlashTrain mode, use a General controller or SetTag Controller to get this value to set the steam flowrate. (B) |
| VapourFlow.Total | Calc | The total required vapour flow to the condenser. (A+B) |
| VapourFlow.Actual | Calc | The total actual vapour flow to the condenser. |
| VapourFlow.Error | Calc | The absolute difference between the Total and Actual vapour flow. This will warn the user if the amount of steam supplied does not equal to the condenser duty requirements. Most common when the condenser is not in demand mode and the steam flow has not been set up to auto adjust. |
| VapourFlow.RelErr | Calc | The relative difference between the Total and Actual vapour flow. This will warn the user if the amount of steam supplied does not equal to the condenser duty requirements. Most common when the condenser is not in demand mode and the steam flow has not been set up to auto adjust. |
Flash Train Macro ModelNote: Extra fields are visible if the unit is part of a Flash Train. These fields are described below. Please refer to Flash Train. | ||
| VapourMassFlowReqd / VQmReqd | Calc | The calculated mass flow of steam required by the Simple Condenser. |
| CondMassFlow / CondQm | Calc | The amount of steam condensed by the Simple Condenser. |
| MinSatPress | Calc | The minimum saturated pressure of steam that could satisfy the heating requirements of the Simple Condenser. |
| FlashTrain | Display | A unique tag assigned to the flash train by SysCAD. Each unit in the flash train will have the same tag in this block. |
| FlashTearBlock | Display | Displays the name of the tear block that is part of the Flash Train. |
| FlashTrainEqp | List | This contains a list of all of the equipment tags in this flash train. the list might be as follows: FT_SC_001 FT_FT_001_C |
| PAdvBase | Input | Additional damping or acceleration for calculated pressure change (DP) for the iteration. DP = DP * PAdvBase when PAdvExtra=0. |
| PAdvExtra | Input | Additional damping or acceleration for calculated pressure change (DP) for the iteration. DP = DP * (PAdvBase + PAdvExtra*(VQmReqd-VQm)/Max(VQmReqd,VQm)). |
Calculated Vapour Condensation(This group of fields are only visible if Method = Mass Condensed, Mass Condensed Tag or Fraction Condensed) | ||
| Condensed.Reqd | Calc | The required amount of material to be condensed. This is the calculated amount based on the user specified mass condensed, mass condensed tag or user specified fraction condensed. |
| Condensed.Actual | Calc | The actual amount of material condensed. |
| Condensed.Error | Calc | The absolute difference between the Required and Actual amount of material condensed. This will warn the user if the amount of condensing species in the feed is less than the user specified mass condensed. |
| Condensed.RelErr | Calc | The relative difference between the Required and Actual amount of material condensed. |
HXCalc
This page is only visible if the HXSizeCalc option is ticked on the first tab page.
| Tag (Long/Short) | Input / Calc | Description/Calculated Variables / Options |
| HX Sizing Calculations | ||
| ModelDuty | Calc | This is the actual duty for the Simple Condenser (thus duty calculated in the first tab page). It is used for all calculations. |
| CalculateWhat | HTC | This allows the user to calculate the required HTC based on Actual Simple Condenser Duty and specifying Area and LMTD. |
| Area | This allows the user to calculate the required Area based on Actual Simple Condenser Duty and specifying HTC and LMTD. | |
| LMTD | This allows the user to calculate the required LMTD based on Actual Simple Condenser Duty and specifying HTC and Area. | |
| HTC | Input/Calc | Heat Transfer Coefficient - This field can be an input or a calculated variable depending on the method selected. |
| Area | Input/Calc | Heat Transfer Area - This field can be an input or a calculated variable depending on the method selected. |
| U*A / UA | Calc | HTC x Area |
| LMTD | Input/Calc | Log Mean Temperature Difference - This field can be an input or a calculated variable depending on the method selected. |
Adding this Model to a Project
Add to Configuration File
Sort either by DLL or Group:
| DLL: | HeatExchange.dll |
→ | Units/Links | → | Heat Transfer: Simple Condenser | |
| or | Group: | Energy Transfer |
→ | Units/Links | → | Heat Transfer: Simple Condenser |
See Model Selection for more information on adding models to the configuration file.
Insert into Project Flowsheet
| Insert Unit | → | Heat Transfer | → | Simple Condenser |
See Insert Unit for general information on inserting units.